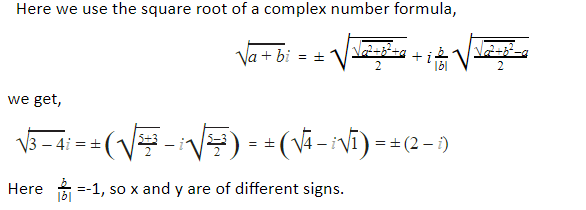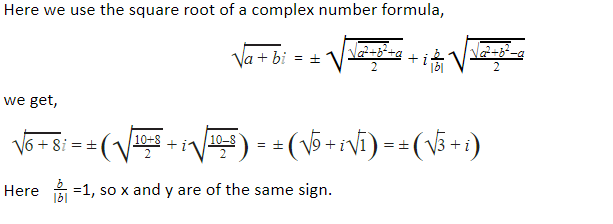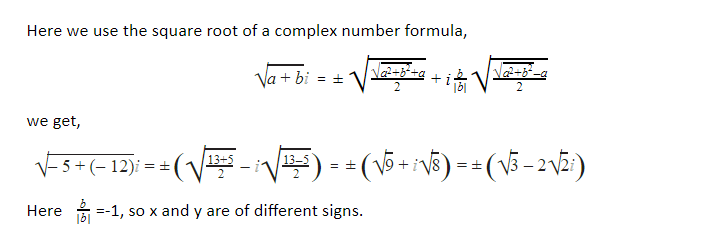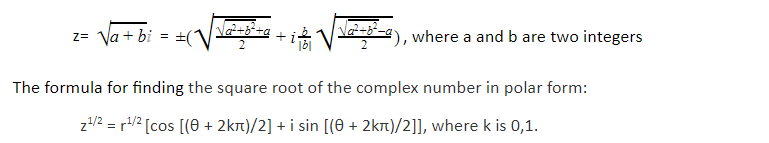Introduction
To understand the square root of a complex number, we should know the definition of a complex number and its representation. A complex number in Mathematics is a number that has a combination of a real part and an imaginary part. We can represent the complex number in rectangular as well as in polar form. In rectangular form, the complex number can be represented as:
Z = A + iB or Z = A + jB
Where,
Z = Complex number;
A = Real part of complex number; and
B = Imaginary part of a complex number.
For example,
Z = 9 + i10 or Z = Z = 9 + j10 is a complex number with 9 as the real part and 10 as the imaginary part of the complex number.
In polar form, the given complex number can be represented as,
Z = R ( cos θ + i sin θ ),
In the above polar form, R cos θ is the real part and R sin θ is the imaginary part of the given complex number.
Rectangular Form and Polar Form relationship of a Complex Number:
We have,
Z = A + iB as a rectangular form of a complex number, and in a polar form, we have Z = R ( cosθ + isinθ).
In comparing real and imaginary parts of rectangular form and polar form, we have:
A = R cos θ and B = R sin θ,
R = (A2 + B2)1/2
tan θ = (B/A)
Representation of the Square Root of a Complex Number in Rectangular form:
As we have the square root of a natural number, e.g. in pairs (square root of x2 is +x and -x), the square root of the complex number A + iB is given by √(A + iB) = ±(a + ib), where a and b are real numbers. So, we can say that the square root of a complex number gives us a pair of complex numbers and the square of these pair of complex numbers gives the original complex number, i.e.
( a + ib )² = A + iB
One of the simple methods to find the square root of a complex number A + iB is to compare the real and imaginary parts of the equation √(A + iB) = a + ib by squaring both sides and then finding the values of a and b. Let’s discuss the procedure for finding the square root of a given complex number.
Let’s assume that the square root of complex number A + iB to be a + ib, i.e. √(A + iB) = a + ib.
Now, on squaring both sides of √(A + iB) = a + ib, we get
[√(A + iB)]² = (a + ib)²
⇒ A + iB = a² + (ib)² + i2ab
⇒ A + iB = a² – b²+ i2ab [As i² = -1]
Comparing real and imaginary parts in the above equation, we have:
A = a² – b², B = 2ab
We know that (a² + b²)² = (a² – b²)² + 4a²b²
⇒ (a² + b²)² = A² + B²
⇒ a² + b² = √(A² + B²) [Because a² + b² is always positive, as we have sum of squares of non-zero real numbers always greater than zero]
Now, we have a² + b² = √(A² + B²) and A =a² – b².
On solving for these two values, we have:
a = ± √{[√(A² + B²) + A]/2}
b = ± √{[√(A² + B²) – A]/2}
As 2ab = B, a and b have the same sign for B > 0, but a and b have opposite signs for B < 0.
Therefore, the square root of complex number A + iB (B ≠ 0) is given by:
√(A + iB) = ± (Z+A²+ iB|B|Z-A²)
where, Z = A + iB and B ≠ 0.
To understand the above concept, let’s take one example of a complex number as Z = 6 + i8, and we will find the square root of this complex number.
In this complex number, we have:
A = 6, B = 8
|Z| = (62+82)1/2 = 10
So, √(A + iB) = ± 10+62+ i8810-62= ±( 2+i )
Representation of the Square Root of a Complex Number in Polar Form :
Z1/2 = R1/2 [cos [(θ + 2kπ)/2] + i sin [(θ + 2kπ)/2]], where k = 0, 1
Conclusion
From the above discussions, we learned the representation of a complex number. We also learned that to find the square root of a complex number, we need to identify the real and imaginary part of the given complex number. We can further use the following formula to find the square root of the given complex number, as √(A + iB) = ± (Z+A2+ iB|B|Z-A2), where Z = A + iB and B ≠ 0. Now, for B < 0, B/|B| = -1, and roots will have opposite signs and for B > 0, B/|B| = 1, roots will have the same sign.
In the polar form, the square root of the given complex number can be calculated by using the relationship, Z1/2 = R1/2 [cos [(θ + 2kπ)/2] + i sin [(θ + 2kπ)/2]], where k = 0, 1.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out