Coordinates geometry
Mathematically speaking, coordinate geometry is an important subfield of geometry since it teaches students how to learn the attributes of geometric forms and helps them present such figures in a two-dimensional plane. In order to get a basic grasp of coordinate geometry, we are going to start by learning about the coordinate plane and the coordinates that can be assigned to a point.
Coordination Plane
A cartesian plane is a useful tool that helps to make locating points in a plane space easier. It does this by dividing the plane space into two dimensions. The coordinate plane is another name for this particular thing. The x-axis is horizontal, and the y-axis is vertical; these are the two axes that make up the coordinate plane. The point where these four axes of coordinates cross is known as the origin(0, 0), and they are used to partition the plane into four quadrants . In addition, every point on the coordinate plane can be represented by the notation point (x, y), where the x value indicates where the point is located in relation to the x-axis and the y value indicates where the point is located in relation to the y-axis.
The Formulas for Coordinate Geometry
The numerous properties of lines and figures that are represented in the coordinate axis can be shown more easily with the use of the formulas that are part of coordinate geometry. The formula for the distance, the formula for the slope, the formula for the midpoint, the formula for the section, and the equation of a line are the formulae that make up coordinate geometry.
The Formula for Distance in Coordinate Geometry
The distance D between two points (x1 and y1) and (x2 and y2) is equal to the square root of the sum of the squares of the difference between the x coordinates and the y-coordinates of the two given points. This formula can also be written as the square root of the difference between the x coordinates and the y-coordinates. The following is a formula that can be used to determine the distance between two places.
D = √(x2-x1)2+(y2-y1)2
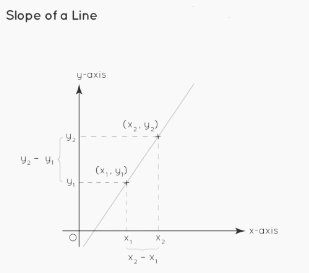
Formula for Slope
The inclination of a line is referred to as the slope of the line. Either the angle that the line makes with the x-axis positive, or the distance between any two places on the line, can be used to calculate the slope of the line. The equation for the slope of a line that is inclined at an angle of with the x-axis in the positive direction is m = Tanθ. The equation for the slope of a line that connects the two points (x1 and y2) and (x2 and y1) is written as
m =(y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
m = Tanθ
m =(y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
Formula for the Midpoint
The formula to find the midpoint of the line that joins the points ( x1, y1) and ( x2, y2) is to create a new point whose abscissa is the average of the x values of the two given points, and whose ordinate is the average of the y values of the two given points. This new point is the midpoint of the line. The midway is situated on the line that joins the two locations and can be found exactly in the middle of where they are placed.
(x,y)=((x1+x2)/2 ,(y1+y2)/2
The Formula for Sections Used in Coordinate Geometry
Find the coordinates of a point that divides the line segment joining the points ( x1, y1 ) and ( x2, y2 ) in the ratio m : n by using the section formula. This formula is useful for finding the coordinates of a point that divides the line segment joining the points ( x1, y1 ) and ( x2, y2). The point that divides the two points that have been supplied can be found on the line that connects the two points and can be found either between the two points or outside of the line segment that runs between the points.
(x,y)=((mx2+nx1)/(m+n), (my2 +ny1)/(m+n))
The Centroid of a Triangle
The point at which the medians of three sides of a triangle meet is known as the centroid of the triangle. (The median is a line that connects the point at the apex of a triangle to the point that is exactly halfway along the opposing side.) The following mathematical method can be used to determine the location of the centroid of a triangle with the following vertices: A ( x1, y1 ), B ( x2, y2 ), and C ( x3, y3 ).
(x,y)=((x1+x2+x3)/3, (y1+y2+y3)/3)
Conclusion
Coordinate geometry is an important subfield of geometry since it teaches students how to learn the attributes of geometric forms and helps them present such figures in a two-dimensional plane.A cartesian plane is a useful tool that helps to make locating points in a plane space easier. It does this by dividing the plane space into two dimensions. The coordinate plane is another name for this particular thing. The numerous properties of lines and figures that are represented in the coordinate axis can be shown more easily with the use of the formulas that are part of coordinate geometry. The formula for the distance, the formula for the slope, the formula for the midpoint, the formula for the section, and the equation of a line are the formulae that make up coordinate geometry.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






