A number that can be found in the real world is referred to as a real number. There are numbers all over the place. Among other things, natural numbers are used to count things, rational numbers are used to represent fractions, Integers are used to measure and irrational numbers are utilized to determine the square root of a number. Temperature. These various forms of numbers make up a collection of real numbers.
Real numbers in algebra Zero (0), the positive and negative integers (-3, -1, 2, 4), and all fractional and decimal values in between (0.4, 3.1415927, 1/2) make up real numbers. Rational and irrational numbers are the two types of real numbers.
Real numbers are represented by points on an infinitely long line known as the number line or real line, on which the points corresponding to integers are evenly spaced. Any real number, such as 8.632, can be computed using a potentially infinite decimal representation, in which each successive digit is measured in unit’s one-tenth the size of the previous one. The complex plane can be thought of as containing the real line, and the real numbers can be thought of as containing the complex numbers.
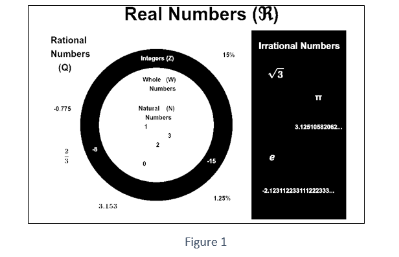
Real Numbers types
The following are instances of several types with real numbers:
Natural Numbers: Natural numbers are the numbers that start at 1 and go up to infinity. They are, for example, 1,2,3,4,5,… Real numbers have a subset called natural numbers. The letter N stands for this.
Whole Numbers: Whole numbers are the numbers 0,1,2,3,… This is a list of natural numbers, which includes 0. Real numbers are also made up of whole numbers. W is the symbol for it.
Integers: Integers are the numbers, –3,–2,–1,0,1,2,3,4,5,.In addition to being a subset of real numbers, integers are also a subset of them. It’s represented by the letter Z.
Rational Numbers: A rational number is one that can be written as pq, where p and q are co-prime integers and q≠0. . Real numbers and rational numbers are both subsets of each other. Q is the symbol for it.
Irrational Numbers: An irrational number is one that cannot be stated in the form pq, where p and q are co-prime integers and q≠0. Irrational numbers are subsets of real numbers. P is the symbol for it.
Real numbers Venn diagram
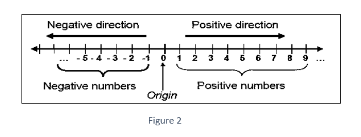
Real number line
The real number line is a horizontal depiction of all real numbers, with Each real number corresponds to a point on the line, and each real number corresponds to a point on the line.
There is a point on the number line that symbolizes zero since the number line represents all real numbers and zero is a real number (called the origin). Positive numbers are represented by points on the line to the right of the origin, whereas negative numbers are represented by points on the line to the left of the origin.
The integers are represented as equally spaced points on the real number line in the accompanying visualization, but the real number line also depicts all real numbers in between the integers and stretching to infinity in both directions.
Real numbers properties
There are a few key properties to remember:
Closure Property: The sum and product of two real numbers is always a real number, according to the closure property. The following is a description of R’s closure property: a, b R, a + b R and ab R
Associative Property: The sum or product of any three real numbers remains the same regardless of the order in which the numbers are grouped. The following is the definition of R’s associative property: If a,b,c R, a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c and a (b c) = (a b) c
Commutative property: The commutative property states that the sum and product of two real numbers remain the same even if the numerals are in reverse order. The following is how R’s commutative property is expressed: If a, b R, a + b = b + a and a b = b a
Distributive Property: Property of Distribution: The distributive property is satisfied by real numbers. Multiplication over addition has the distributive property a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c) while multiplication over subtraction has the distributive property a × (b – c) = (a × b) – (a × c)
Conclusion
In this article we study that all the numbers on the number line are real numbers, and there are an unlimited number of them. Both rational and irrational numbers are included in real numbers. Their types and categories are significant since they can provide you with further information regarding the issue you’re investigating.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






