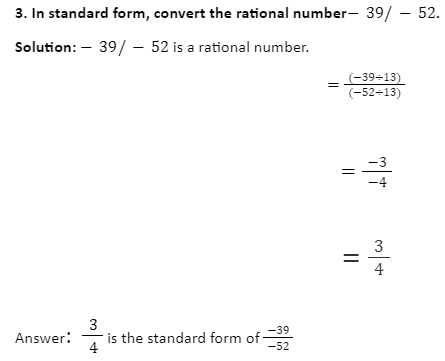
When a rational number is expressed in standard form, it indicates the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1, and the denominator is a positive integer. Rational numbers are those that can be represented in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q is not equal to zero. As a result, if 4/6 is a rational number, its standard form will be 2/3, because we can no longer solve 2/3.
The standard form of a rational number allows us to more precisely calculate the value. For example, 20/25 can be stated as 4/5, 10/20 as 1/2, and so on.
We rationalize fractions in math to represent them in standard forms. There are two parts to fractions: a numerator and a denominator. When the numerator and denominator of a fraction are co-prime, it is said to be in standard form. Rational numbers include all integers & fractions. Once we’ve rationalize the denominators of rational numbers, adding and subtracting them is simple.
Or
A rational number a/b is said to be in standard form if there are no common factors between the numerator and denominator other than1, and the denominator b is positive.
How to write a number in rational form
After integers, rational numbers are one of the most prevalent types of numbers we learn in math.These numbers are in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. Because of the basic structure of numbers, p/q form, most individuals find it difficult to distinguish between fractions and rational numbers. Fractions are made up of whole numbers, whereas rational numbers have integers in the numerator and denominator.
A rational number is one that can be written as p/q, where p and q are integers and q is less than zero. Q or Q denotes the set of rational numbers. 1/4,2/5, 0.3, 3/10, 0.7 & 7/10, 0.151515 are some examples.
Procedure for converting a rational number to standard form
The numerator and denominator of a rational number are the same. If the Highest Common Factor (H.C.F.) of the numerator and denominator is 1, a rational number is said to be in standard form. Now the question is, how can every rational number be converted to its standard form?
The following procedures are followed to express a given rational number in standard form:
- To find the rational number, use the formula below.
- Check whether the rational number’s denominator is positive or not. If the denominator is negative, multiply or divide both the numerator and the denominator by -1 to make the denominator positive.
- Find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator absolute values.
- Divide the provided rational number’s numerator and denominator by the GCD (HCF) produced in point 3. The resulting rational number is the provided rational number’s standard form.
Rational numbers in standard form examples
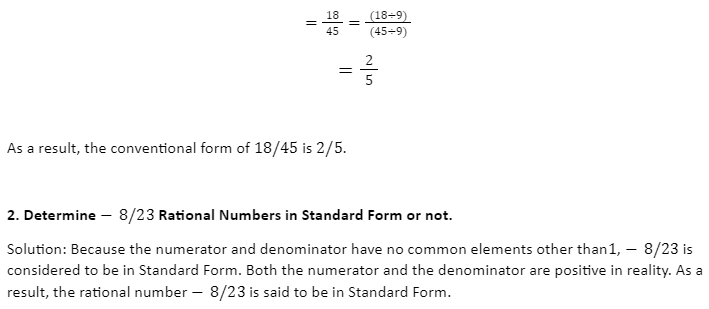
- What is the standard form of the rational number 18/45?
Solution: 18/45 is a rational number.
In the given rational number, look for the denominator. You don’t have to do anything because it’s positive.
Find the GCD of the absolute values of numerator 18 and denominator 45 after that.
GCD(18, 45) = 9
Simply divide both the numerator and denominator by 9 to convert the supplied rational number 18/45 to standard form.
Conclusion
When the numerator and denominator of a rational number have no common factor other than 1, and the denominator is a positive integer, the rational number is in standard form. Standard form is frequently referred to as the simplest or lowest form. In the conventional form, rational numbers assist us in determining the value in a more specific manner.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out