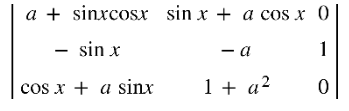Before heading to the properties, here’s an introduction to determinants!
A determinant is a scaling factor for a matrix’s array of numbers that can provide information about these values as components of a vector or linear equation system. When performing these linear algebra procedures, keep in mind that we can only calculate the determinants of squared matrices or those with the same number of rows and columns.
To get the value of a determinant with the fewest calculations, properties of determinants are required. The properties of determinants are based on the elements, row, and column operations, and they help determine the value of the determinant rapidly.
Types of Determinants:
There are commonly 3 types of determinants:
1. First Order Determinant: This is used to calculate the determinant of a one-dimensional matrix. If [a] = A, the determinant of A will be ‘a’.
2. Second-Order Determinant: For matrices of order 2, this is utilized. The determinant of an order 2 matrix can be found by multiplying the diagonally opposite components of the matrix and then determining the difference between their products.
3. Third Order Determinant: To find the determinant of a matrix of order 3, add the product of the diagonally opposite components of the matrix, then, remove the sum of elements perpendicular to the line segment.
The approaches described above are commonly used to solve maximal issues in determinants. The above-discussed methods can be utilized for more complex questions too by increasing the determinant along the row of the matrix with the most zeroes.
What Are the Properties of Determinants?
The features of determinants aid in quickly calculating the value of a determinant with the fewest steps and calculations possible. The following are the 7 most important properties of determinants.
1. Property of Interchange:
When the rows or columns of a determinant are swapped, the determinant’s value remains unchanged.
A = A’ =
Det(A) = Det(A’)
As a result of this property, if the rows and columns of the matrix are swapped, the matrix is transposed, and the determinant value and the determinant of the transposition are both equal.
2. Sign Property: If any two rows or columns are swapped, the sign of the determinant’s value changes.
A =
R1 ⬄ R3
B =
If the row or column is swapped once, the determinant’s value changes the sign. To obtain matrix B, the first row of matrix A has been swapped with the third row, and we have Det(A) = -Det(A) (B). If the determinant’s value is D and the rows or columns are swapped n times, the new determinant’s value is (-1)nD.
3. Zero Property: If the elements in any two rows or columns are the same, the determinant’s value is zero.
A =
The items in the first and second rows are identical in this case. As a result, the determinant’s value is zero.
Det(A) = 0
4. Multiplication Property: If each of the elements of a given row or column is k times the earlier value of the determinant, the deciding value becomes k times the earlier value of the determinant. If each element of a given row or column is multiplied by a constant k, the determining value becomes k times the earlier value of the determinant.
A =
B =
Det(B) = k× Det(A)
The second row of A is multiplied with a constant k. Here, k = 4.
The second row’s elements are multiplied by a constant k, and the determinant value is multiplied by the same constant. This characteristic aids in the extraction of a common factor from each determinant row or column. In addition, the value of the determinant is 0 if the corresponding elements of any two rows or columns are equal.
5. Sum Property: The determinant can be expressed as a sum of two or more determinants if a few items of a row or column are expressed as a sum of words.
6. Property of Invariance: When each element of a determinant’s row and column is multiplied by the equimultiples of the elements of another determinant’s row or column, the determinant’s value remains unchanged. This can be stated as a formula as follows:
Ri→Ri+αRj+βRk or Ci→Ci+αCj+βCk
7. Triangular Property: The value of the determinant is equal to the product of the components of the diagonal of the matrix if the elements above and below the main diagonal are both equal to zero.
=
= a1.b2.c3
Conclusion
We’ve covered the fundamental properties of determinants.
You are more likely to earn good scores in your examination if you have a thorough comprehension of matrix-related topics.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





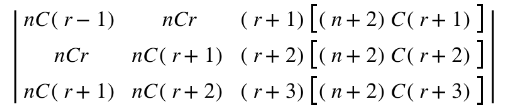
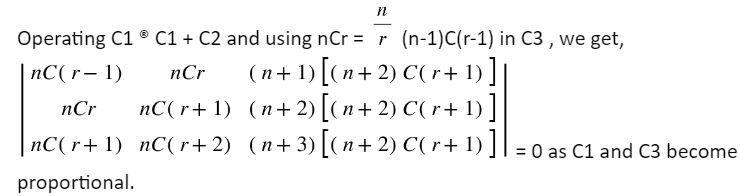
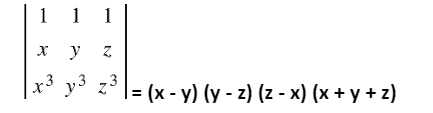

 is independent of x.
is independent of x.