Properties Straight Line
Straight lines have the following qualities.
- The length of a straight line is endless. We will never be able to calculate the distance between the line’s two extreme points
- There are no areas and no volume in a straight line. However, it has an infinite length
- A one-dimensional figure is a straight line
- A single point can have an endless number of lines passing through it, but only one line travels through two points.
Equation of a Straight Line
A linear equation is a straight line equation. Based on known variables, angles, and constants, a straight line on a cartesian plane can have various representations. The slope of a straight line dictates the line’s direction and indicates how steep it is. Rise over run is calculated as the difference in y coordinates divided by the difference in x coordinates. A straight line equation can take many different forms. These are the details:
Straight Line Equation in General
A straight line’s general equation can be written as
ax + by + c = 0, where
- x and y are variables, while a, b, and c are constants.
- -a/b is the slope.
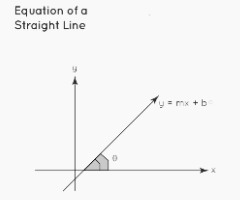
Y-intercept and Slope Form
A straight line with slope m = tanθ and y-intercept b is given by: y = mx + b, where m is the slope and θ is the angle formed by the line with the positive x-axis.
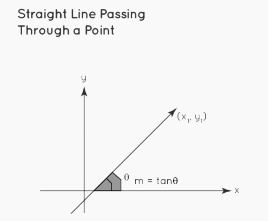
Slope Point form
A straight line passing through a point (x1, y1) with slope m =tanθ, where is the θ angle formed by the line with the positive x-axis, is given by: y – y1 = m(x – x1)
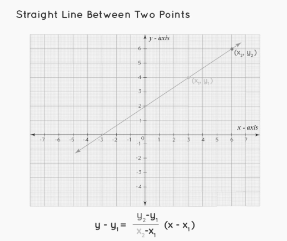
Two Points Form
In the two-point form, a straight line passing between points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is represented by: y – y1 = [(y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1)] (x – x1).
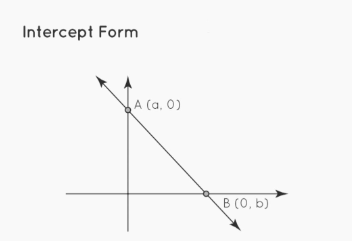
Intercept Form
The intercept form of a straight line with x-intercept a and y-intercept b, as illustrated in the diagram below, where point A is on the x-axis (vertical here) and point B is on the y-axis (horizontal here), is x/a + y/b = 1.
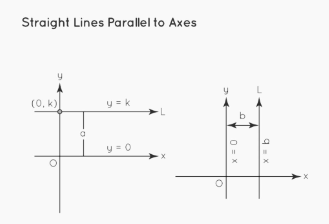
Lines Parallel to the X-axis or Y-axis Equation
y = ±a, where an is the equation of a line parallel to the x-axis.
a is the line’s distance from the x-axis. If an is above the x-axis, it has a positive value, and if it is below the x-axis, it has a negative value.
x =±b, where b is the equation of a line parallel to the y-axis.
The distance between the line and the y-axis is b. If b is on the right side of the y-axis, it has a positive value, and if it is on the left side, it has a negative value.
The figure below shows lines parallel to the x- and y-axes, respectively.
Slopes of Various Types
The slope of a line is the angle created by a line with a positive x-axis. With the x-axis, different lines form different angles. A line can have slopes that are positive, negative, zero, or infinite. Let’s look at a few examples.
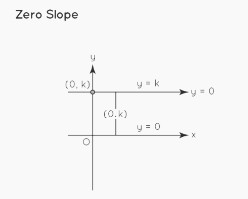
Slope of 0
The slope of a line that creates a 0° angle with the x-axis is 0. m = tanθ is the formula for calculating the slope of a line.
Here, θ = 0° . As a result, m = tan0 = 0. As a result, a line with a slope of 0 is perpendicular to the x-axis.
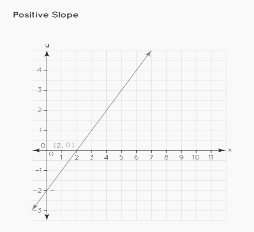
Slope: Positive
The slope of a line is positive if it produces an angle with the x-axis between 0 and 90 degrees.
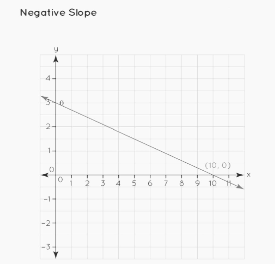
Slope is Negative
The slope of a line is negative when it makes an angle with the x-axis between 90° and 180°.
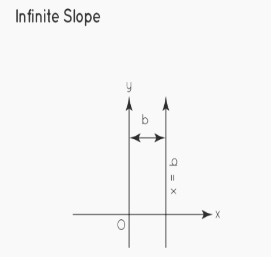
Slope Without End
The slope of a line that forms a 90° angle with the x-axis or is parallel to the y-axis is neither specified nor infinite.
The slope of a line is defined as m = tanθ.
Here, θ = 90° . The slope m = tan 90° is unknown. As a result, the infinitely sloped line is parallel to the y-axis.
Important Points to Remember About Straight Lines
Here is a list of some important points to consider when studying straight lines:
Three non-collinear points cannot be crossed by a straight line.
When two lines l and m intersect, the relationship l = k x m holds, where k is a real number.
tanθ =(m2 – m1)/(1 + m2 m1) can be used to compute the acute angle between two lines with slopes m1 and m2, where m2 > m1.
Conclusion
The length of a straight line is endless. We will never be able to calculate the distance between the line’s two extreme points.There are no areas and no volume in a straight line. However, it has an infinite length.A one-dimensional figure is a straight line.A single point can have an endless number of lines passing through it, but only one line travels through two points.A linear equation is a straight line equation. Based on known variables, angles, and constants, a straight line on a cartesian plane can have various representations. The slope of a straight line dictates the line’s direction and indicates how steep it is.A straight line with slope m = tanθ and y-intercept b is given by: y = mx + b, where m is the slope and θ is the angle formed by the line with the positive x-axis.Three non-collinear points cannot be crossed by a straight line.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





