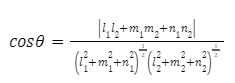The mathematical study of three-dimensional shapes in three-dimensional space, known as three-dimensional geometry, requires the use of three coordinates: x-coordinate, y-coordinate, and z-coordinate. To pinpoint the precise location of a point in a three-dimensional space, you will need to consider three criteria. Due to the fact that there are many problems pertaining to three-dimensional geometry on the JEE, this topic is quite important. In this section, the fundamental ideas of geometry using three-dimensional coordinates are discussed, which will assist the reader in comprehending the various operations that can be performed on a point in a three-dimensional plane.
Three Dimensional Geometry – Important Concepts
In three-dimensional geometry, a point is represented by its three coordinates at all times. When it comes to three-dimensional geometry, the most significant ideas to understand are the direction ratio, the direction cosine, the distance formula, the midpoint formula, and the section formula. The fundamental ideas of three-dimensional geometry are broken down into the following categories.
Direction Ratios
A vector is used to represent the point A, which has the coordinates a, b, and c. The position vector is written as.
𝑂𝐴 =𝑎𝑖 +𝑏𝑗 +𝑐𝑘
which also includes the direction ratios a, b, and c. This proportion illustrates the vector line in relation to the x-axis, the y-axis, and the z-axis, respectively. Additionally, the direction cosines can be derived with the assistance of these direction ratios.
Direction Cosine
The cosine function determines the relationship between any given vector or line in a three-dimensionalspace and any one of the three axes. This line subtends an angle with the x-axis, the y-axis, and the z-axis, and the cosine of that angle is the direction cosine. If the angles that are subtended by the line when it is parallel to the three axes are,, and, then the direction cosines are respectively
𝐶𝑜𝑠𝛼=𝑎 / √𝑎²+𝑏²+𝑐²
,𝐶𝑜𝑠𝛽=𝑏 / √𝑎²+𝑏²+𝑐²
The cosines of a vector’s respective directions
𝐴=𝑎𝑖+𝑏𝑗+𝑐𝑘
We may demonstrate that l2 + m2 + n2 = 1 by using the direction cosines, which are also denoted by the letters l, m, and n.
Distance Formula
The distance between two points 𝑥1,𝑦1,𝑧1
and 𝑥2,𝑦2,𝑧2
is the shortest distance, and it is equal to the square root of the summation of the square of the difference between the x coordinates, the y-coordinates, and the z-coordinates of the two given points. This is the simplest form of the formula for calculating the distance between two points. The following is a formula that can be used to determine the distance between two places.
𝐷= √ 𝑥1−𝑥2²+𝑦1−𝑦2²+𝑧1−𝑧2²
Mid-Point Formula
The formula to locate the point that is exactly halfway down the line that joins the points 𝑥1,𝑦1,𝑧1
and 𝑥2,𝑦2,𝑧2
is a new point whose abscissa is the average value of x for the two points that were supplied, and whose ordinate is the average value of y for the two points that were given. The midway is situated on the line that joins the two locations and can be found exactly in the middle of where they are placed.
𝑥,𝑦,𝑧=(𝑥1+𝑥2) / 2+(𝑦1+𝑦2) / 2+(𝑧1+𝑧2) / 2
Section Formula
It is possible to discover the coordinates of a point 𝑥1,𝑦1,𝑧1
and 𝑥2,𝑦2,𝑧2
that cuts the line segment in the ratio m:n.
𝑥,𝑦,𝑧= (𝑛𝑥1+𝑚𝑥2) / 𝑚+𝑛+(𝑚𝑦1+𝑛𝑦2) / 𝑚+𝑛+(𝑛𝑧1+𝑚𝑧2) / 𝑚+𝑛
The point that divides the two points that have been given is located on the line that connects the two points, and it can be reached either by going between the two points or by going beyond them on the line.
The Angle Between Two Lines
The next topic that will be covered is the calculation of the angle formed by two straight lines, which will be presented in the following section. It is important to keep in mind that when we speak of the angle that exists between two lines, in most circumstances, we are actually talking to the angle that exists between two lines that intersect. This is because the angle formed by two lines that are perpendicular to one another is always 90 degrees, while the angle formed by two lines that are parallel to one another is always 0 degrees.
As a result, we will now investigate the process of calculating the angle formed by two lines that intersect with one another. You will have a better understanding of the geometric implication of this computation after looking at the accompanying figure.
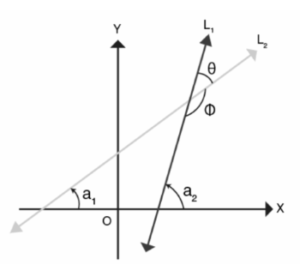
Let us assume that the direction cosines of the two lines are, respectively, (l1, m1, n1) and (l2, m2, n2) It is important to keep in mind that the cosines of a line’s direction are, in fact, the angles that exist between the line and any one of the three coordinate axes. Now, let’s say the angle between the lines is represented by the symbol. Take note of the following formula:
Using the formula below, you can simply get the angle in terms of Sin if that is what you wish to do.
𝑆𝑖𝑛2𝜃=1−𝐶𝑜𝑠2𝜃,
and then you can replace Cos 𝜃 using the formula above.
Conclusion
In three-dimensional geometry, a point, a line, or a plane can be represented by making reference to the x-axis, the y-axis, and the z-axis, respectively. All of the ideas that are fundamental to coordinate geometry in two dimensions are present in three-dimensional geometry as well.
For the purpose of describing three-dimensional space, the Cartesian coordinate system is utilised. This system consists of an origin and six open axes, with +z and –z being perpendicular to the x-y plane. Octants are the names given to the eight distinct portions that result from the division of space into three planes by these axes.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out