In vector theory, the parallelogram law of vector addition is a method for determining the sum of two vectors that is based on the parallelogram law of vector addition. We will look at two laws of vector addition – the triangle law of vector addition and the parallelogram law of vector addition – in this chapter. This law of vector addition is used to add two vectors when the vectors to be added form two adjacent sides of a parallelogram formed by combining the tails of the two vectors to produce the parallelogram itself. The diagonal of the parallelogram is used to calculate the sum of the two vectors in this case.
Throughout this article, we will look at the parallelogram law of the addition of vectors, including its formula and explanation, as well as examples of its application. We will study how to apply the law with the assistance of many instances in order to gain a better knowledge of the topic.
Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition
A vector addition operation can be used to determine the sum of two vectors, and the parallelogram law of vector addition is a law that makes it easier to determine the sum vector that results from the operation. Assume that a fish is swimming from one side of a river to the other side of the river in the direction of the vector Q, and that the river water is flowing in the direction of the vector P, as shown in the image below.
Since there are two velocities in play – that of the fish and the flow of water in the river (which will be a separate velocity) – the net velocity of the fish is the total of the two velocities. As a result, the fish will move in a different direction along a vector that is equal to the sum of the two velocities. The net velocity may now be calculated by considering these two vectors as the neighbouring sides of a parallelogram and applying the parallelogram law of vector addition to determine the resultant total vector.
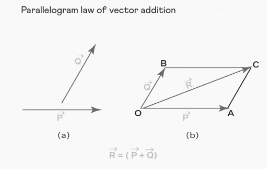
The Formula for the Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition
Consider two vectors P and Q that are at an angle of one another. The sum of the vectors P and Q is represented by the vector R, which is the resultant sum vector, when the parallelogram law of vector addition is applied to the vectors P and Q. If the resultant vector R forms an angle with the vector P, the following formulas can be used to calculate its magnitude and direction:
|R| = √(P2 + Q2+ 2PQ cos θ)
β = tan-1[(Q sin θ)/(P + Q cos θ)]
Proof of the Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition
First, let us look at the formal formulation of the parallelogram law of vector addition:
The following is a formal statement of the Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition: If two vectors can be represented completely by the two adjacent sides (both in magnitude and direction) of a parallelogram drawn from a point, then their resultant sum vector can be represented completely by the diagonal of the parallelogram drawn from that point.
Then, in order to demonstrate the parallelogram law’s formula, we will use two vectors P and Q, which are represented by the two neighbouring sides OB and OA of the parallelogram OBCA, respectively, and represent the two adjacent sides of the parallelogram. The angle formed by the two vectors is denoted by the symbol. When these two vectors are added together, the consequent sum vector R is formed by drawing a diagonal from the same vertex O of the parallelogram to the opposite vertex O of the parallelogram, and the resultant sum vector R is formed by making an angle of with respect to the vector P.
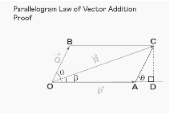
Extend the vector P until it intersects with the vector D so that CD is perpendicular to OD. Due to the fact that OB is parallel to AC, the angle AOB is equal to the angle CAD because they are matching angles, i.e., angle CAD =. In order to begin, we will first create a formula to determine the size of the resultant vector R. (side OC).
In right-angled triangle OCD, we have
OC² = OD² + DC²
⇒ OC² = (OA + AD)² + DC² — (1)
In the right triangle CAD, we have
cos θ = AD/AC and sin θ = DC/AC
⇒ AD = AC cos θ and DC = AC sin θ
⇒ AD = Q cos θ and DC = Q sin θ — (2)
Substituting values from (2) in (1), we have
R² = (P + Q cos θ)² + (Q sin θ)²
⇒ R² = P² + Q²cos2θ + 2PQ cos θ + Q²sin2θ
⇒ R² = P² + 2PQ cos θ + Q²(cos2θ + sin2θ)
⇒ R² = P² + 2PQ cos θ + Q² [cos2θ + sin2θ = 1]
⇒ R = √(P² + 2PQ cos θ + Q²) → Magnitude of the resultant vector R
Next, we will determine the direction of the resultant vector. We have in right triangles ODC,
tan β = DC/OD
⇒ tan β = Q sin θ/(OA + AD) [From (2)]
⇒ tan β = Q sin θ/(P + Q cos θ) [From (2)]
⇒ β = tan-1[(Q sin θ)/(P + Q cos θ)] → Direction of the resultant vector R
Important Points to Remember About the Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition
The parallelogram law of vector addition is used when two vectors are linked at their tails to form the adjacent sides of a parallelogram. When the two vectors are parallel, the magnitude of the resultant vector can be calculated by simply combining the magnitudes of the two vectors in the same direction.
The triangle law of vector addition and the parallelogram law of vector addition are equal, and the resultant vector has the same value as the original vector.
Conclusion
A vector addition operation can be used to determine the sum of two vectors, and the parallelogram law of vector addition is a law that makes it easier to determine the sum vector that results from the operation. Consider two vectors P and Q that are at an angle of one another. The sum of the vectors P and Q is represented by the vector R, which is the resultant sum vector when the parallelogram law of vector addition is applied to the vectors P and Q.If two vectors can be represented completely by the two adjacent sides (both in magnitude and direction) of a parallelogram drawn from a point, then their resultant sum vector can be represented completely by the diagonal of the parallelogram drawn from that point. When the two vectors are parallel, the magnitude of the resultant vector can be calculated by simply combining the magnitudes of the two vectors in the same direction.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






