An orthogonal trajectory of the family is a curve that cuts every member of a particular family of curves at right angles. It is not required for the curve to pass through each family member. When they cross, however, the angle formed by their tangents at each point of intersection is 90°.
Definition
A curve that crosses any curve of a given pencil of (planar) curves orthogonally is called an orthogonal trajectory in mathematics.
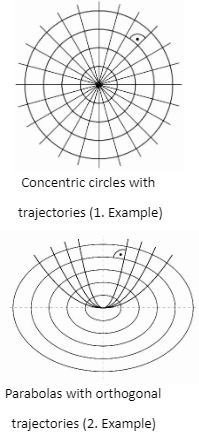
For example, the lines through the common center of a pencil of concentric circles are orthogonal trajectories (see diagram).
Solving differential equations provides suitable approaches for determining orthogonal paths. The traditional method starts with a first-order ordinary differential equation and solves it with variable separation. Both steps may be challenging, if not impossible. In such instances, numerical approaches must be used.
In mathematics, orthogonal trajectories are utilised as curved coordinate systems (i.e. elliptic coordinates) or as electric fields and associated equipotential curves in physics.
An isogonal trajectory is one in which the trajectory intersects the specified curves at an arbitrary (but fixed) angle.
Orthogonal
Orthogonal is the same as perpendicular in fundamental geometry. If two lines or curves intersect at their point of intersection, they are orthogonal. If the dot product of two vectors v and w in the real plane R2 or the real space R3 is 0, they are orthogonal. In the more abstract context of the n-dimensional real space Rn, this criterion has been used to define orthogonality.
If the inner product of two elements v and w of an inner product space E is 0, they are called orthogonal. If every element of V is orthogonal to every element of W, two subspaces V and W of E are said to be orthogonal. Any symmetric or differential k-form, as well as any Hermitian form, can be defined using the same definitions.
Determination of the Orthogonal Trajectory
In Cartesian Coordinates
The pencil of curves is usually assumed to be implicitly supplied by an equation.
(0):F(x,y,c)=0 1. Example
X²+y²-c=0 2. Example
y=cx² ⇔ y-cx²=0
where c is the pencil’s parameter. If the pencil is represented explicitly by the equation y=f(x,c), the representation can be changed to an implicit one: y-f(x,c)=0. All essential derivatives are assumed to exist for the following consideration.
Step 1.
Implicit differentiation for x produces
Step 2. is now assumed that equation (0) can be solved for parameter c, and that equation (0) can thus be removed (1). The first-order differential equation is obtained. This is satisfied by the curves pencil provided.
Step 3. The orthogonal trajectory satisfies the differential equation of first order because the slope of the orthogonal trajectory at a location (x,y) is the negative multiplicative inverse of the slope of the provided curve at this point.
Step 4: Hopefully, an appropriate approach can solve this differential equation.
Separation of variables is appropriate in both cases. Solutions include:
Trajectories
A trajectory, also known as a flight path, is the path taken by a mass in motion through space as a function of time. A trajectory is described by Hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates in classical mechanics; thus, a complete trajectory is defined by position and momentum at the same time.
A projectile or a satellite could be the mass. An orbit, for example, is the route taken by a planet, asteroid, or comet as it travels around a central mass.
A trajectory is a time-ordered set of states of a dynamical system in control theory (see, for example, the Poincaré map). A trajectory is a sequence (fk(x))k∈ℕ of values calculated by iteratively applying a mapping f of x its source in discrete mathematics.
Physics of Trajectories
The path of a projectile, such as a thrown ball or rock, is an example of a trajectory. The item travels exclusively under the influence of a uniform gravitational force field in a drastically simplified model. For a rock thrown over short distances, such as on the moon’s surface, this can be a decent estimate. The trajectory is shaped like a parabola in this simple approximation. In general, while determining trajectories, nonuniform gravitational forces and air resistance must be taken into account (drag and aerodynamics). The discipline of ballistics focuses on this.
The development of Kepler’s laws was one of Newtonian mechanics’ most impressive breakthroughs. The trajectory of a moving object in the gravitational field of a point mass or a spherically-symmetrical extended mass (such as the Sun) is a conic section, commonly an ellipse or a hyperbola. [a] Although if a comet passes close to the Sun, it is also influenced by other forces such as the solar wind and radiation pressure, which modify the orbit and cause the comet to eject material into space, this agrees with observed orbits of planets, comets, and artificial spacecraft to a reasonable degree.
Newton’s idea later evolved into classical mechanics, a branch of theoretical physics. It makes use of differential calculus mathematics (which was also initiated by Newton in his youth). Countless scientists have contributed to the growth of these two areas over the years. In science and technology, classical mechanics became a prominent proof of the power of rational thought, or reason. It aids in the understanding and prediction of a wide range of phenomena, including trajectories.
Consider a mass mm particle travelling in a potential field V. In physical terms, mass denotes inertia, while the field V denotes external forces of a particular type known as “conservative.” There is a way to infer the related force that would act at each relevant point, say from gravity, given V at each relevant position. However, not all forces can be described in this way.
Conclusion
In mathematics, orthogonal trajectories are utilised as curved coordinate systems (i.e. elliptic coordinates) or as electric fields and associated equipotential curves in physics. An isogonal trajectory is one in which the trajectory intersects the specified curves at an arbitrary (but fixed) angle.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






