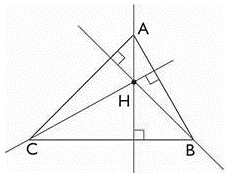
The point of intersection of altitudes drawn perpendicular from the vertex to the opposing sides of a triangle is known as an orthocenter. The orthocenter of a triangle is the point at where the triangle’s three altitudes intersect. The following are the three most important aspects of an orthocenter. The center of all right angles from the vertices to the opposing sides, i.e. the altitudes, is known as the orthocenter. The intersection point of three angles drawn from the three vertices of a triangle is known as the orthogonal intersection point. The study of a triangle’s many features in relation to its other dimensions necessitates the use of an orthocentre.
Orthocentre of triangle
The orthocentre is the point where all of the triangle’s elevations intersect. The letter H is commonly used to denote the orthocenter.
Take a look at the image below:
The letter ABC is shaped like a triangle, the letter ABC is made up of three parts, each of which is represented by a triangle (AE, BF, and CD), ABC has three elevations. The intersection point H is the orthocenter, and ABC has three vertices (text A, B, and C).
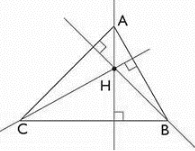
Figure: 1
Orthocentre Properties
The orthocentre is the point where the altitudes drawn from the triangle’s vertices to the opposite sides intersect.
- In the case of an acute triangle, it is located within the triangle.
- It is located on the outside of an obtuse triangle.
- It is located at the right angle’s vertex in a right-angled triangle.
- For all three perpendiculars, the product of the sections into which the orthocentre splits an altitude is the equivalent.
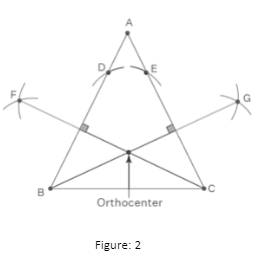
How to Create an Orthocentre?
To construct a triangle’s orthocentre geometrically, we must do the following:
- Determine the perpendicular connecting any two vertices on opposite sides.
- Use vertex C as the center and a radius equal to the side BC to draw the perpendicular or altitude. On the opposing sides, AB and AC, draw arcs.
- At F, connect the intersecting arcs from B and D. Join the CF.
- Draw intercepted arcs from points C and E to G in the same way. Join the BG.
- For the sides AB and AC, CF and BG are altitudes or perpendiculars, respectively.
- The orthocenter is the point where any two vertices of a triangle intersect.
- As a result, locate the position where the two altitudes overlap.
- H is referred to as the triangle’s orthocentre at that position.
Orthocentre formula
The orthocentre formula can be used to find the coordinates of a triangle’s orthocentre. Consider the triangle PQR represented in the diagram below.
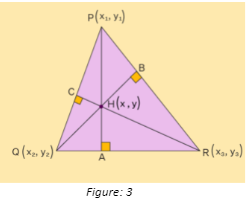
PA, QB, RC are the perpendicular lines drawn from the three vertices.
H(X-Y) is the place where the triangle’s three elevations meet.
Step -1 using the formula, find the slope of the triangle’s sides:

The orthocenter of a triangle can be computed by solving the two equations for any given values.
Conclusion
The study of a triangle’s many features in relation to its other dimensions needs the use of an orthocentre. The orthocenter of a triangle is used to determine the triangle’s type. An acute triangle is one in which the Orthocenter of the triangle is located at the center of the triangle. An obtuse triangle is one in which the Orthocenter is located outside of the triangle.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out