- While learning 3D Geometry, a line and a plane are two basic terms that can be defined. A line can be determined uniquely under two conditions when it passes through a point and has a direction or passes through two different points.
- A plane can be identified as a plane under three conditions.
- The first one is when there is a normal to the plane, and the plane’s distance from the origin is known.
- In the second condition, there is a normal to the plane, and the coordinates of a point lying on the plane are known.
- The last condition is when there are a set of three non-collinear points whose coordinates are known.
Defining terms
- A point in 3D is represented as P(x,y,z). Three coordinates define the position of a point concerning the x,y and z-axis, respectively.
- As its name suggests, the unit vector is a vector that has a length of 1.
- When a vector has one of its ends fixed and the other linked to a moving point, it is termed a position vector.
- Normal to a plane is a line that is perpendicular to the plane. It is represented using the letter n. Considering it as a unit normal vector, the notation used will be n.
- The triangular law of vector addition is extremely helpful in deducing results and simplifying complex calculations. This law states that when two adjacent sides of a triangle represent two vectors, the resultant is represented by the third side of the triangle taken in the opposite direction to the other two vectors.
- The dot product of vectors involves multiplication and addition of the respective coefficients of both vectors and results in a scalar.
- The dot product of two perpendicular vectors will always be zero.
Drawing the plane
- To understand the normal form, it is necessary to first visualise the plane. Consider the below diagram,
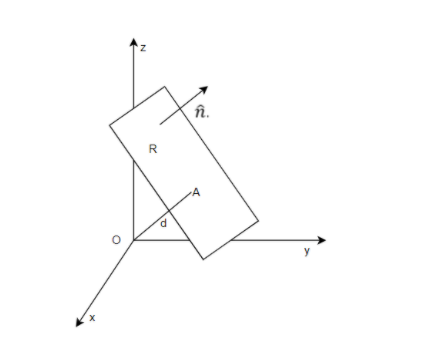
- Here, the normal unit vector to the plane is drawn. It is also visible that the plane is at a distance of d units from the origin, which is represented by point O. The point on the plane is represented by A.
- There is an arbitrary point on the plane represented by R and the position vector of this point is r.
Derivation: A vector form
- The terms and the diagram are well understood. So, the next step is to derive the equation of the plane in this condition. Or, in other words, the normal form of the plane.
- Observing the diagram, notice that the unit normal to the plane, n and the vector representing the distance to the plane, OA are parallel. This is because both these vectors are perpendicular to the plane.
- This observation helps us write the vector OA as the product of direction given by the unit normal vector, n and the magnitude given by distance d.
OA=d.n
- The vector OR is already defined by its position vector, so OR=r.
- Join the points O, A, R to form a triangle.
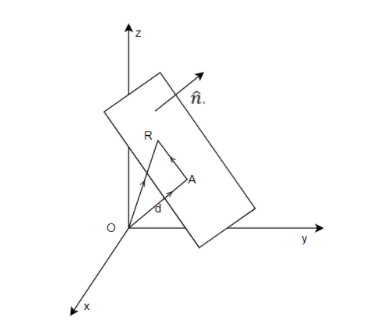
- Now, applying the triangular law of vector addition,
OA+AR=OR
AR=OR–OA
- Substituting the known values in the above-obtained equation,
∴AR=r-d.n
- It is evident from the diagram that vectors AR and OA are perpendicular to each other as they meet at a right angle.
- It indicates that their dot product would be zero.
AR.OA=0
- Again, substituting the respective vectors in the above equation,
r-d.n.d.n=0
- The term d is a scalar and is the distance from the origin to plane hence it cannot be zero,
d≠0.
r-d.n.n=0
- Taking the dot product,
r.n–d.n.n=0
- Since the second term has a product of the unit vector, it can be simplified using the fact that the dot product of unit vectors is one.
∴r.n-d=0
It can also be written as
r.n=d
- Hence, this is the vector form.
Derivation: Cartesian form
- The difference in Cartesian form is that instead of the position vector, the coordinates of the point R are to be considered. So, it will be taken as R(x,y,z).
- So, it can be written as OR=r=xi+yj+zk.
- The direction cosines of unit normal vector n would be l,m,n, respectively.
- So, it can be written as n=li+mj+nk.
- The vector form of the normal form of the plane is r.n=d.
- So, substituting the above results in it,
xi+yj+zk.li+mj+nk=d
- Taking the dot product,
lx+my+nz=d
- Hence, this is the Cartesian form.
Conclusion
The equation of a plane in the normal form is obtained as r.n=d. The terms
r, n and d represent the position vector of an arbitrary point on the plane, the normal unit vector to the plane and the distance from the origin to the plane, respectively. If we consider a plane passing through the origin, then the value of d would be 0. The normal form of the plane modifies as r.n=0 or lx+my+nz=0. The importance of the normal form of a plane lies in the applications that include formulating the plane’s equation for the given conditions, converting from one form to the other, or finding the missing parameters when the equation of the plane is given.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






