The implicit function theorem is a mechanism in mathematics that allows relations to be transformed into functions of various real variables, particularly in multivariable calculus. It is possible to do so by representing the relationship as a function graph. An individual function graph may not represent the entire relation, but such a function on a constraint of the relation’s domain may exist. The implicit function theorem provides a sufficient condition to ensure the existence of such a function.
Theorem of implicit function
According to the implicit function theorem, if that point is not a critical point, we can find coordinates near that point such that the function is a linear function in these coordinates. This is a very useful observation for reducing pseudo differential operators.
If a function with n equations is given, such that fi (x1,…, xn, y1,…, yn) = 0, where i = 1,…, n, or we can also represent as F(xi, yi) = 0, the implicit theorem states that, under a fair condition on the partial derivatives at a point, the m variables yi are differentiable functions of the xj in some section of the point. Because we cannot express these functions in closed form, the equations implicitly define them.
Example:
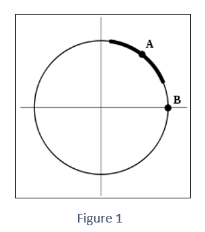
If we define f(x, y) = x2 + y2, then the equation f(x, y) = 1 cuts out the unit circle as the level set (x, y) | f(x, y) = 1. The unit circle cannot be represented as a graph of a function of one variable y = g(x) because there are two options for y for each choice of x (-1, 1), namely 1-x2
However, a portion of the circle can be represented as the graph of a one-variable function. If we allow it,gx=1-x2 If −1 ≤ x ≤ 1 is given, then the graph of y=g1(x) gives the circle’s upper half Similarly ifg2 x=-1-x2 then there is the graph of y=g2(x) gives the circle’s lower half.
The implicit function theorem’s purpose is to tell us the existence of functions like g1(x) and g2(x)even when we can’t write down explicit formulas. It ensures that g1(x) and g2(x) are differentiable, and it even works when we don’t have a formula for f. (x, y).
Proving the implicit function theorem
Letf:Rn+mRm be a continuously differentiable function, and let Rn+m have coordinatesx,y. Fix a point a,b=(a1,…,an,b1,…,bm) with fa,b=0 where 0Rm is the zero vector. If the Jacobian matrix Jf,ya,b=fiyj(a,b) is invertible, then there exists an open setURncontaining a such that there exists a unique continuously differentiable function g:URm such that ga=b, and fx,g(x)=0 for all x∈U. Moreover, denoting the left-hand panel of the Jacobian matric shown below as: Jf,xa,b=fixj(a,b),the The matrix product yields the Jacobian matrix of partial derivatives of g in U.
gixjxm×n=-Jf,yx,gxm×m Jf,xx,gxm×n
Proof for 2D Case:
Suppose F:R2R is a continuously differentiable function defining a curve Fr=Fx,y=0. Let(x0,y0) be a point on the curve. The statement of the theorem above can be rewritten for this simple case as follows:
Theorem-If ∂y∂x|(x0,y0)≠0 then for the curve around(x0,y0) we can writey=f(x), where f is a real function.
Proof: We write the differential of F through partial derivatives because F is differentiable: F=graduation F.dr=∂F∂xdx+∂F∂ydy.
Since we are restricted to movement on the curve dF=0 and by assumption F∂x≠0 around the point(x0,y0) ( Since ∂F∂y is continuous at(x0,y0)and ∂y∂x|(x0,y0)≠0).
As a result, we have the following first order ordinary differential equation::xF<∞, yF<∞,yF≠0. From this we know that xFyF Lipschitz continuous in both x and y. Therefore, by Cauchy- Lipschitz theorem, there exists unique y(x) that is the solution to the given ODE with the initial condition Q.E.D.
Importance of implicit function theorem
- An implicit function theorem is a tool in multivariable calculus that allows relations to be converted to functions with multiple real variables using a graphical representation of the function
- The implicit function theorem seeks to convey the presence of functions such as g1(x) and g2(x)even when explicit formulas cannot be defined
- The implicit function theorem ensures that the functions g1(x) and g2(x)can be differentiated
- The implicit function theorem also applies when there is no formula for the function
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the implicit function theorem is a tool in mathematics, more specifically in multivariable calculus that allows relations to be converted to functions of several real variables. It accomplishes this by representing the relationship as a graph of a function. There may not be a single function whose graph can represent the entire relation, but there may be such a function on a restriction of the relation’s domain. The implicit function theorem provides a sufficient condition to ensure the existence of such a function. The infinite-dimensional implicit function theorem is used to demonstrate the existence of solutions to nonlinear partial differential equations and to parameterize the space of solutions.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out