The functions which take one or more operations as a single input function are considered as composite functions. For instance, if a function took an element from set A to B and another function took an element from set B to C then the composite function would take the element directly from A to C. In simple words, we can create a new function by composing one function into another function.
Sum, difference, product and quotient of functions
Any two real numbers are combined by arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, product and division likewise functions can be combined too. Consider the functions f(x) = 2x -3 and g(x) = x2 – 4.
If we perform the basic addition we will get, f(x)+ g(x) = 2x -4 + x2 – 4 = x2 +2x -8
Difference = f(x) – g(x) = 2x -4 – x2 + 4 = -x2 +2x
Product = f(x) * g(x) = (2x-3) (x2 -4) = 2×3 -8x -3×2 + 12
Quotient = f(x)/g(x). This case is a bit different as it puts more restrictions on the operation. x ≠ ±1
Finding Domain of the function
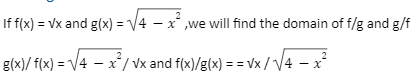
the domain of f is [ 0, ∞] and for g is [ -2,2]
and the domain intersection would be [0,2]
Readers must note that the domain of f/g includes x = 0 but not include x= 2 because x = 2 yields a zero in the denominator, but the domain of g/f involves x = 2 but not involves x = 0 because x = 0 yields a zero in the denominator.
Composition of functions
Let us considered f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x +1
Then composition of f(x) with g(x) will be:
F(g(x)) = f( x+1) = (x+1)2
This composition is denoted as (f ∘ g)(x) and reads as “f composed with g.”
Properties of composite function: Associative
Associative functions are always composable. This means, no matter where the brackets are located in a function, it makes no difference to the overall result of the function.
if f, g, h are composable then f ( gh(x)) = (fg)h (x)
Commutative Property
Commutativity is when swapping the order of the function’s composition, does not affect it, e.g. xy = yx .
One to one property
When there is only a single output for every single input then it is one to one property.
Inverse function
An inverse must exist for a composite function, therefore, there cannot be an output for which there does not exist an input
Examples
Let say g(x) is used as the input of f(x) then the composite function is written as (f ∘ g)(x)
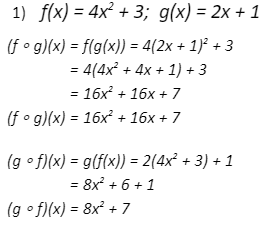
Consider another example,
- F (x) = 3x +2 and g(x) = 5x -1. If h(x) = fg(x) , find value of h(2)
G (2) = 5(2) -1
= 10-1
= 9
Now this output will serve as input
F (9) = 3(9) +2 = 29
H (2) = 29
- Find (g ∘ f) (x) if, f(x) = 6 x² and g(x) = 14x + 4
Substitute x in g(x) = 14x + 4 with 6 x²
⟹g [f(x)] =14 (6 x²) + 4
= 84 x² + 4
- For f(x) = 3x + 4 and g(x) = 5, find (f ◦ g) and (g ◦ f).
Solutions: (f ◦ g) (x) = f(g(x)) = f (5) = 3(5) + 4 = 19
(g ◦ f) = 5 itself.
Conclusion
Algebraic operations can be performed on functions. When functions are combined the output of the inner function becomes the input of the outer function. The domain of a composite function consists of those inputs in the domain of the inner function which correspond to the outputs of the inner function that are in the domain of the outer function. Just as we combine functions to form a composite function, we can decompose composite functions into simpler functions too.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






