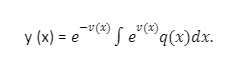An I.F is a function that is chosen to aid in the solution of a differential equation.
It’s typically employed to solve ordinary differential equations, but it’s also used in multivariable calculus to turn an inexact differential into an exact differential by multiplying by an I.F.
An I.F is a function that can be multiplied by an ordinary differential equation to make it integrable.
For example, a linear first-order ordinary differential equation of type
dy/dx+p(x)y(x)=q(x),
where p and q are given continuous functions, can be made integrable by letting v(x) be a function such that
v (x) = ∫p(x)dx
and
dv(x)/dx=p(x).
Then evx would be the I.F such that multiplying by y (x) gives the expression
d/dx y(x)] =evx + p(x) y(x)]
=evxq(x)
using the product rule.
Integrating both sides with respect to X then gives the solution
Integrating factor method:
The function chosen to solve the given differential equation is referred to as the I.F.
It’s most often used in first-order ordinary linear differential equations.
When a differential equation of the form is given;
dy/dx + P(x) y = Q(x)
then the I.F is defined as;
µ = e∫P(x)d(x)
Where P(x) (the function of x) is a multiple of y and μ denotes I.F.
The I.F approach can be used to solve linear, first-order differential equations of the form:
dy/dx+a(x)y=bx.
The functions a(x) and b(x) are continuous. An equation expressed in the manner described above is said to be written in standard form.
The I.F approach is a method for solving linear, first-order differential equations.
Solving First Order Differential Equation Using I.Fs:
Consider an ordinary differential equation (o.d.e.) that we want to solve in order to determine how the variable y is affected by the variable x. The highest derivative involved in a first derivative equation is a first derivative.
If it’s also a linear equation, this means that y can appear in each term as the derivative dy dx OR as a single factor of y.
The integrating factor approach can be used to solve a linear first order o.d.e.
P(x) can be identified after expressing the equation in standard form. The equation is then multiplied by the “integrating factor” as follows:
IF= e∫P(x)dx
This factor is defined so that the equation becomes equivalent to
: d/dx (IF y) = IF Q(x), whereby integrating both sides with respect to x, gives:
IF y = I.F Q(x).dx
Finally, division by the integrating factor (IF) gives y explicitly in terms of x, i.e. gives the solution to the equation.
The I.Fs approach can be used to solve a first-order differential equation of the form dy/dx + y P(x) = Q(x).
To determine the general solution of the differential equation, we can follow the instructions below:
Step 1: Simplify the first-order differential equation and express it as dy/dx + y P(x) = Q(x)
Step 2: Determine the I.F given by, I.F. = e∫P(x) dx
Step 3: Multiply the differential equation dy/dx + y P(x) = Q(x) by the I.F to obtain d(y × I.F.)/dx = Q(x) × I.F.
Step 4: Now, integrate both sides of the equation d(y × I.F.)/dx = Q(x) × I.F. to get the general solution.
Proof:
We derive the formula for the I.F used to solve linear ODEs of the form,
dy/dx + a(x)*y = b(x) ………(1)
Let µ be the I.F.
Consider equation (1) × µ, µ*dy/dx + µa(x)y = µb(x) ………… (2)
Using product rule to simplify the LHS of equation 2.
The product rule states: d/dx(uv) = u dv/dx + v du/dx.
Equating terms in the product rule with LHS of equation (2) gives:
u = µ dv/dx = dy/dx, v = y and du/dx = µa(x).
The first and fourth expressions give du/dx = dµ/dx = µa(x).
Solving this equation using separation of variables gives:
Z 1 µ du = Z a(x)dx
µ = µZ a(x)dx¶ ,
The expression for the I.F of a linear ODE.
Now after applying multiplication rule,
d/dx(µy) = b(x)µ.
Now we know µ we can integrate this equation w.r.t. x and solve to find y
Generalizing I.Fs:
To begin, consider the standard form of a linear first-order DE
dy/dx + P(x)y = Q(x).
Multiplying by dx,
we get [P(x)y − Q(x)]dx + dy = 0.
If this equation were exact, we would have P(x) = 0, which is not generally true. However, let us multiply the equation by the I.F
µ(x) = P(x)dx: [µ(x)P(x)y − µ(x)Q(x)]dx + µ(x)dy = 0.
Now the exactness condition is µ(x)P(x) = µ 0 (x), which you may recall is exactly how we derived the formula for the I.F.
Conclusion:
The process of splitting a polynomial into a product of simpler polynomials is known as the Integrating factor. This is done in the hopes of making the polynomial easier to deal with and solve. Any polynomial, regardless of degree, can be factorised using the I.F method.
The method of I.F factorization consists of several parts. The first step is to locate all of the polynomial factors. This can be accomplished by a variety of approaches, including trial and error and the factor theorem.
Once the components have been identified, the following step is to integrate them all. This is accomplished by multiplying the factor by each polynomial term before integrating the result.
The final step is to combine all of the integrals into a single integral after all of the components have been integrated. The product rule for integrals can be used to do this. The final solution can be discovered once the integral has been completed.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out