The differential equation is basically about the rate of change of one quantity with respect to another quantity. So, the differential equation is defined as the equation which has a derivative of the dependent variable with respect to an independent variable.
The ordinary differential equation is a differential equation that has a derivative of the dependent variable with respect to only one independent variable. The differential equation which involves derivatives with respect to more than one independent variable is called a partial differential equation.
The depth study of the differential equation helps us to study modern scientific investigation. Here I am going to list some basic concepts of differential equations, how to form a differential equation, first-degree differential equation, and a few applications of the differential equation.
Differential Forms
As discussed above there are two types of the differential equation. The first is an ordinary differential equation and the second one is a partial differential equation.

This equation includes variables as well as derivatives of the dependent variable y with respect to independent variable x. Hence, This equation is referred to as a differential equation.

Order and Degree of Differential Equation
Order of a differential equation is the order of the highest order derivative of the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable.
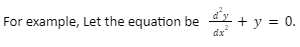
Here the highest derivative will be second order. Therefore, the order of the equation is 2.
Degree of the differential equation can be studied when the differential equation must be a polynomial equation in derivatives i.e. y’, y’’, y’’’ etc.
For example, let us assume the differential equation be,
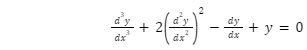
Since the above equation is a polynomial equation in y’’’. So, the degree of such an equation is defined. The degree of the above equation is one.
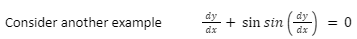
Here, the equation is not a polynomial equation in y’ and the degree of such a differential equation cannot be defined.
The order and degree of a differential equation are always positive integers.
General and Particular Solutions of Differential Equations
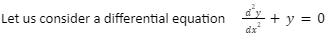
The solution of this differential equation is function $ that will satisfy it, which means when function $is substituted for the unknown y which is a dependent variable in the given differential equation, L.H.S is equal to R.H.S.
The curve y=$(x) is called the solution curve of the given differential equation.
Function $ consists of two arbitrary constants and it is called a general solution of a given differential equation. If a function $contains no arbitrary constants but only the particular values of the parameters, then it is called a particular solution of a differential equation.
Formation of Differential Equation
Let us consider the equation x2+y2=r2
By putting different values of r, we will get different members of family i.e.
x2+y2=16, x2+y2=25 etc.
Hence, the equation represents a family of concentric circles centered at the origin and having different radii.
f given family F1 of curves depend on only one parameter then it is represented by the equation in the form of F1x,y,a=0.
If the given family F2 of curves depend on parameters a, b then it is given by an equation in the form of F2x,y,a,b=0.
The order of the differential equation representing a family of curves is the same as the number of arbitrary constants present in the equation corresponding to the family of curves.
Linear Differential Equations

Homogeneous Differential Equation
A function F(x, y) is said to be a homogenous function of degree n if Fƛx, ƛy=ƛnF(x,y) for any nonzero constant ƛ.
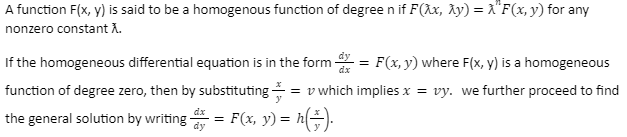
Conclusion
An equation that includes a derivative of the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable is defined as a differential equation. To form a differential equation from any given function, we differentiate the function successively the number of times the arbitrary constants in available the given function and then eliminate the arbitrary constants. One of the methods to solve the differential equation involves the variable separable method. It is used to solve such an equation in which variables can be separated i.e. terms containing y should remain with dy and terms containing x should remain with dx.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






