Each term in a geometric progression (GP) has a constant ratio to the one before it. It’s a one-of-a-kind progression. Every time we want to find the next term in the geometric progression, we must multiply with a fixed term known as the common ratio, and every time we want to find the preceding term in the progression, we must divide with the same common ratio. In a G.P., any two consecutive numbers have the same ratio, which is known as the constant ratio. It is usually represented by the letter ‘r.’ As a result, if we have a G.P., we can have finite or infinite geometric progressions. It can have a positive or negative common ratio.
General Term
Any geometric series’ general term, or nth term, can be found using a formula. The formula is xn = a times r to the n – 1 power.
In this formula, xn represents the number in that series. x4 represents the fourth term in our sequence. The term in question is represented by the letter n. If n is 10, we are looking for the tenth term in our sequence. The common ratio (r) is the multiplication constant used to calculate each successive integer or term in the geometric sequence. We enter our a and r for our geometric sequence when we want to use this formula.
Representations and the formulas
Sum of Finite Geometric Progression
If a geometric progression has a finite number of terms, the sum of the geometric series is calculated using the formula:
In geometric progression (also known as geometric series), the sum is given by

Sum of Infinite Geometric Progression
An infinite geometric series sum formula is used when the number of terms in a geometric progression is infinite.
In an infinite geometric progression, the number of terms approaches infinity (n = ∞). Only the range -1.0 < (r ≠ 0) < +1.0 can be used to define the sum of infinite geometric progression.
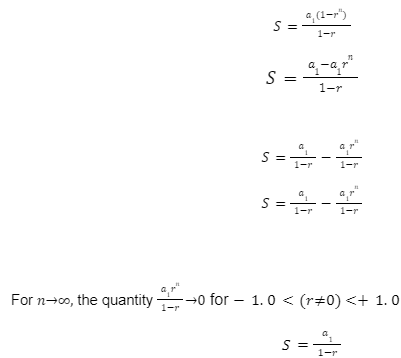
Conclusion
As a result, the ratio of the two phrases that follow one another in this particular sequence is always the same number. The term geometric progression refers to this kind of series. In addition, the sequence known as the geometric progression is the one in which the first term does not equal zero, and each succeeding term is obtained by multiplying the term that came before it by a constant amount. Geometric sequences (with a common ratio that is not equal to 1, 1 or 0) exhibit either exponential growth or exponential decay. This is because the common ratio does not equal 1, 1 or 0. (with common difference 11). T.R. Malthus used this finding as the mathematical basis for his Principle of Population that he developed. It is important to note that the two types of progression are related to one another. For example, taking the logarithm of each term in a geometric progression that has a positive common ratio results in an arithmetic progression. Exponentiating each term of an arithmetic progression results in a geometric progression.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






