What are Differential Equations?
A differential equation is an equation that has a function, such as F(x), and one or even more derivatives, such as dy/dx. The physical quantities are commonly represented by the functions of a differential equation, while the rate of change of the physical quantities is given by the derivatives. A differential equation is a mathematical expression that describes the connection here between function and also its derivatives. When we examine y as a function of x, a differential equation is one that incorporates the derivatives of y with respect to x (or the differentials of y and x) with or without variables x and y.
Order of Differential Equations
It represents the highest order of the derivative. Here are some of the examples

First Order Differential Equation
The example of a first-order differential equation is given below. There is only one first derivative dy/ dx present.
For example – (dy/dx) = tan x
The first order derivatives are represented by
dy/dx =f(x,y)= y’
Second Order Differential Equation
Here is an example of a second-order differential equation. It is represented as :
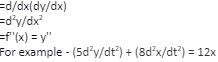
Degree of Differential Equations
- The highest-order derivatives power is called the degree of the differential equation.
- The differential equation may be in the polynomial form in that the highest order of differential power is called a degree.
- Choose the positive integer of the find about the degree.
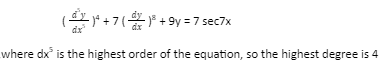
Types of Differential Equation
There are two types of differential equations. They are
- Ordinary differential equation
- Partial differential equation
Ordinary Differential Equations
- ODE – A differential equation comprising one or even more functions from one independent variable with their derivatives is known as an ordinary differential equation (ODE).
For example here are some derivatives y’+y”+y”’+y””+……… y^n concerning x
- The ordinary differential equation is further classified into two. They are
Example: (d2y/dx2) + (dy/dx) = 3y tan x
- Homogeneous differential equation
- Nonhomogeneous differential equation
Homogeneous Differential Equation
- The equation that contains differentiation, set of variables and function(x, y) is called a homogeneous differential equation.
- The homogeneous differential equation should have the same power for the given variables (x, y)
Homogeneous differential equation
f(x,y).dy + g(x,y).dx = 0
where x and y are variable having same degree
dx/dy = F(x,y)
Homogeneous function
f (δx,δy) = δ n f(x,y)
where δ is non zero constant
- There is no constant term present in the homogeneous differential equation. Only in the linear differential equation, you can see the constant term
- If we remove the constant term from the linear differential equation, then the equation would turn into the homogeneous differential equation
- No variable is present in the special functions like logarithm of trigonometric
Here are some example

You can substitute x and y in all the above examples to prove the homogeneous differential equation.
- x = δx
- y = δy
Substitute x/y = v or x= vy when the homogeneous differential equation is in the form of dx/dy=f(x,y) and has the homogeneous function f(x,y).
Non- Homogenous Differential Equation
It is much similar to that of a linear equation and the order of the differential equation is not similar.
For example, the differential equation of the form (dy/dx) + Py = Q where P, Q are the constant or the function of x
The general solution is given as
Y * ( integrating factors) = Q* (integrating factors).dx + c
where integrating factors = epdx
Formation of Partial Differential Equations
For more than one function and more than one independent variable is used. It is called Partial differential equation(PDE)
Here are a few examples that are
- 5𝛿u/ dx + 7𝛿u/𝛿xy = 0,
- 21𝛿2u/𝛿x2 + 8𝛿2u/𝛿x2 = 0
Conclusion :
The connection between both the variables x and y that is produced after eliminating the derivatives (i.e., integration) or where the connection includes an arbitrary constant to signify the order of an equation is the basic solution of a differential equation. An arbitrary constant appears in the solution of first-order differential equations, while two arbitrary constants appear in the solutions of second-order difference equations. The solution of the differential equations is derived by giving specific values to the arbitrary constant.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






