Different rules of exponents exist in mathematics. All of the exponent rules are used to solve many mathematical problems that need repeated multiplication processes. Exponent laws make multiplication and division easier to comprehend and solve problems with. We’ll go over the six most important laws of exponents in this post, along with plenty of examples.
Basic Concepts:-
Exponents are used to indicate the multiplication of a single integer over and over again. For instance, 6 × 6 × 6 can be written as 6³. The exponent in this case is ‘3,’ which represents the number of times the number 6 has been multiplied. The base number is 6, which is the number that is being multiplied. Exponents, often known as powers, refer to the amount of times a number can be multiplied. If the power is 5, it signifies the base number has been multiplied five times. Here are a few examples:
5⁴ = 5 × 5 × 5 × 5
8² = 8 × 8
9⁵ = 9 × 9 × 9 × 9 × 9
If a number ‘a’ is multiplied by itself n times, it is written as an, with a as the base and n as the exponent.
i.e., an = a × a × a × a × a × a × × ……….. × a (n times)
Basic Laws of Exponents:-
As previously stated, different laws or rules apply to different participants. Some of the most important exponent laws are as follows:
Product with same bases:-
According to this law, for any non-zero term p,
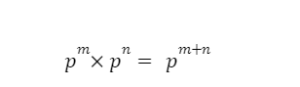
Where , m and n are real numbers.
Illustration 1:
Find 4⁴ × 4⁷
Here, 4⁴ × 4⁷ = 44+7=411
Illustration 2:
Find (-2)⁶ × (-2)²
Here, (-2)⁶ × (-2)² =-26+2=-28
We might say that the law applies to both positive and negative terms. As a result, m and n can be any integer.
Quotient with same base:-
According to this law, for any non-zero term p,
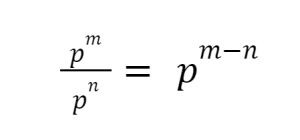
Where, m and n are integers.
Illustration:
Find the value when 10⁵ is divided by 10⁷
According to the question,
105107=105-7=10-2=1100
Power raised to a power:-
According to this law for any non-zero term p
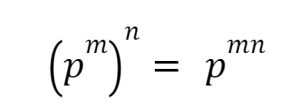
Where, m and n are integers.
Illustration:
Express 16⁴ as a power with base 2.
Solution: We have, 2×2×2×2 = 16 = 2⁴
Therefore, 16⁴ = (2⁴)⁴ = 2¹⁶
Product to a power:-
If the power is the same for two or more different bases, then this rule applies.
The rule is as follows:
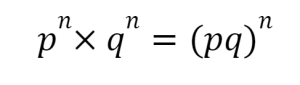
Where, p and q are non-zero terms and n is an integer.
Illustration:
Simplify 6⁴ × 3⁴
Here, 6⁴ × 3⁴
= (6×3)⁴ = 18⁴
Quotient to a power:-
The fraction of two separate bases with the same power is expressed by this law as;
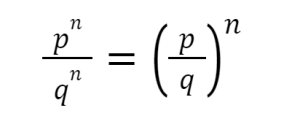
Where, p and q are non-zero terms while n is an integer.
Illustration:
Find the quotient of 8⁴ and 2⁴
As per question, 8424=824=44
Zero power law:-
When the power of an integer equals zero, its value is equal to 1, according to this rule.
i.e., p⁰ = 1
where p is a non-zero term.
Negative exponent rule:-
According to this rule, if the exponent is negative, we can make it positive by entering the same value in the denominator while the numerator is set to 1.
The law is stated as:
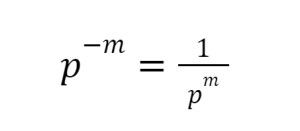
Where, p is a non-zero term and m is an integer.
Illustration:
Find the value of 2-2
Here, 2-2=122=14
Scientific notation of exponents:-
The traditional form of writing very big or very small numbers is scientific notation. In this, decimal and powers of ten are used to write numbers. When a number from 0 to 9 is multiplied by a power of ten, it is considered to be written in scientific notation. The power of ten is a positive exponent when the number is greater than one, and a negative exponent when the number is less than one. Let’s look at how to write numbers with exponents in scientific notation:
After the first digit of the number from the left, add a decimal point. We don’t need to put a decimal if a number has only one digit, omitting zeros.
Multiply that amount by a power of ten so that the power equals the number of times the decimal point is shifted.
We can write any number in standard form with exponents by following these two simple procedures, for example;
5740000 = 5.74 × 10⁶
45783201 = 4.5783201 × 10⁷
Applications of exponents:-
Exponents are used in a variety of ways. The following are a few examples of exponent applications:
Exponents are commonly employed in computer games, weighing scales, and other similar applications.
Exponents are used in scientific scales such as the pH scale and the Richter scale.
They’re useful for estimating area, volume, and other measurement-related difficulties.
Science, engineering, economics, accounting, and finance are the most common fields in which they are employed.
They’re frequently used to symbolize the memory of a computer or laptop.
Conclusion:-
An exponent of a number indicates how many times a number is multiplied by itself. For example, 3⁴ denotes a four-fold multiplication of three. 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 is its expanded form. The power of the number is also known as that number. It can be any type of number, including whole numbers, fractions, negative numbers, and decimals.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






