What exactly is Exponential Distribution?
The exponential distribution is a continuous probability distribution in probability theory and statistics that often concerns the amount of time until a given event occurs. It is a continuous and independent process in which events occur at a constant average pace. The important feature of the exponential distribution is that it is memoryless. The exponential random variable can have a greater number of small values or fewer larger variables. The amount of money spent by a customer on a single trip to the grocery, for example, follows an exponential distribution.
Formula for Exponential Distribution
If a continuous random variable, say X, has the following probability density function, it is said to have an exponential distribution:
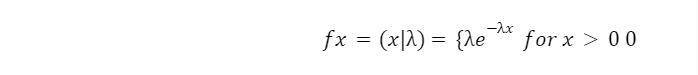
Where λ is referred to as the distribution rate.
λ is defined as the average time/space between Poisson Distribution events (successes).
Mean and Variance of Exponential Distribution
Mean:
The integration by parts method is used to compute the mean of an exponential distribution.
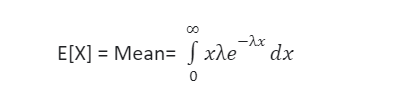
Solving the equation it comes 1/ λ
Variance :
To calculate the variance of the exponential distribution, we must first calculate the second moment of the exponential distribution, which is given by:
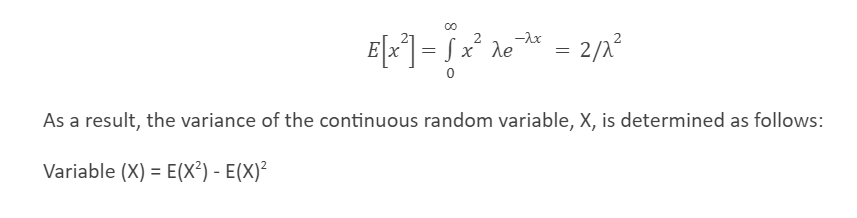
Now, if we substitute the mean value and the second moment of the exponential distribution, we get,

Memoryless Property of Exponential Distribution.
The conditional behaviour of exponential random variables is described by the memoryless property. It’s one of our important findings, which we’ll apply to the queueing system solution.
Let’s consider that X has an exponential distribution with a parameter. Assume we know X > t. What is the likelihood?
P(X > s + t | X > t)
This type of issue arises commonly in queueing systems when the time between events is of concern. Assume, for example, that the service times for jobs in our system are exponentially dispersed. What is the likelihood that a job that has been running for one hour will continue to run for more than two hour?

The conditional probability appears to be t-independent! An exponential random variable’s chance of exceeding the value s + t given t is the same as the variable’s chance of exceeding the value s + t.In our employment example, the likelihood of a job running for one hour longer is the same as regardless of how long it’s been running, the likelihood that it ran for one hour at first.
Because the past has no bearing on its future behaviour, the exponential distribution is memoryless.
Every instant is analogous to the start of a new random period, which has the same distribution regardless of how long it lasts.
Exponential is only a memoryless continuous random variable.
When Should You Use an Exponential Distribution?
Instead of jumping right to the formulas, we always start with the “why.” If you understand why something is the way it is, it will stick with you and you will be much more inclined to use it in your own area of work.
Why did we need to invent the concept of Exponential Distribution?
To forecast the amount of time until the next occurrence (i.e., success, failure, arrival, etc.).
For example, we’d like to forecast the following:
- The time it takes for a customer to finish browsing and make a purchase at your store (success).
- The time it will take until the hardware on AWS EC2 fails (failure).
- The amount of time you must wait for the bus to come (arrival).
Applications for Exponential Distribution
The exponential distribution is a common type of continuous distribution. It aids in determining the amount of time that has passed between the events. It is utilised in a variety of applications, including dependability theory, queuing theory, and physics. The exponential distribution can be used to model the following fields:
- The exponential distribution can be used to calculate the distance between mutations on a DNA strand.
- Calculating the time it will take for the radioactive particle to decay.
- It aids in determining the height of various molecules in a gas at a stable temperature and pressure in a uniform gravitational field.
- It aids in calculating the highest monthly and annual values of regular rainfall and river outflow volumes
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






