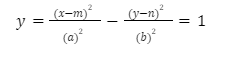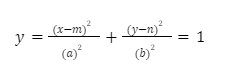An equation of a conic section can be defined as a mathematical curve which has a set of points P, the distance of which from the focus remains a constant integral or rational or real multiple of the distance from P to what is called as the directrix of that conic.
The parabola, hyperbola, ellipses, and even circle are classified as types of ellipse. Conic sections are generated when an intersecting plane runs across the cone. A cone contains two identical shaped top/bottoms called nappes which resemble a party hat. When the plane is perpendicular to the axis around which the cone can revolve, the conic section is a circle.
Let us go through some basic definitions to understand the equation of conic sections better.
Some Basic Definitions:
Asymptote: It is defined as a straight line in which a curve tends to reach/approaches arbitrarily closely as it tends to go to infinity.
Locus: Locus is defined as the collection of all those points whose co-ordinates can satisfy the condition of the curve or conic section. Locus refers to all the surface points taken together.
Focus: Focus is defined as a point that is used to build a conic section. All the rays reflected from the conic section converge or meet (plural: foci).
Nappe: Nappe is defined as the one half of the double cone, which can be thought of as two inverted party hats placed tip to tip on one another.
Conic section: Conic section is defined as a mathematical curve that is obtained by the surface intersection of a plane with two nappes.
Directrix: Directrix is defined as a line (or even a line segment) that is used to build a conic section. Varying conic sections have different numbers of directrix, whereas a parabola has one, ellipses and hyperbolas both possess two (plural: directrices).
Eccentricity: It is defined as (represented by e), a mathematical relational function associated with all of the conic sections. It can be visualised as the deviation any conic section takes from being circular lamina. The eccentricity of any conic section can also be put as the ratio of distances from any point on a particular conic section to its own focus and the orthogonal distance of that point from the nearest directrix of that conic section.
The value of e never changes for any conic section. This property is used to extrapolate a general definition for a variety of conic sections. The range value of e is often used to determine which conic section we are talking about. The eccentricity of a circle (which is a conic section) is zero. Two similar or identical conic sections are those which possess the same eccentricity.
e = 1 : Parabola
e > 1 : Hyperbola
e <1 =Parabola
Writing Equations of Conic Sections
- Parabola– A parabola is defined as a mathematical figure which is the collection of all points whose distance from a fixed (not necessarily stationary) point, which is termed as the focus, is equal to the distance measured from a fixed line (maybe a line segment), which is termed as the directrix. The point that lies midway between the focus of the parabola and the directrix of the parabola is termed as the vertex of the parabola.
![]()
- Hyperbola – A hyperbola is defined as a mathematical curve, more specifically, a smooth curve that happens to lie in a plane, which can be quantified by the specific geometric properties it has or by the possession of specific equations it yields a solution set for. A hyperbola is composed of two pieces, termed as components/branches, resembling two infinite bows as if they are mirror images of each other. If the centre is at (m,n)
3. Ellipse – An ellipse is a mathematical figure which consists of all the points with centre at (m,n)
Applications of Conic Sections
The conic sections have useful applications in various fields of study, specifically those dealing with shapes and its description. For example, when the conic section is applied in astronomy, it helps us describe the shapes of the orbits of objects/planets/galaxies in the infinite cosmos.
Two massive mass objects interact with each other in space by Newton’s law of universal gravitation, but they move in orbits that are in or closely resemble the shape of conic sections. This leads to the formation of parabolic, elliptical, or even hyperbolic orbits.
Our satellite positioning is highly dependent on the knowledge of these equations of the conic section. Equations of conic sections, therefore, are in a way responsible for our television, internet service, and live streaming activities.
Conclusion
The conic sections are special mathematical curves that possess great relevance in improving our understanding of astronomy and satellite placement. These curves are represented by specific equations and are derived from the intersection of a plane with certain specifics with two nappes.
Conic sections provide us with valuable insight for geometrical exploration and conventional quantitative and qualitative knowledge of distance and symmetry.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out