Functions are balanced between domain and co-domain. Domain is a part of a function as range, the difference between both is the domain is all the values that go into a function, and the range is all the values that come out. The concept of function is really important in mathematics as it captures the idea of correspondence of one quantity with another.
In other words the domain of a function f(x) is the set of all values for which the function is defined
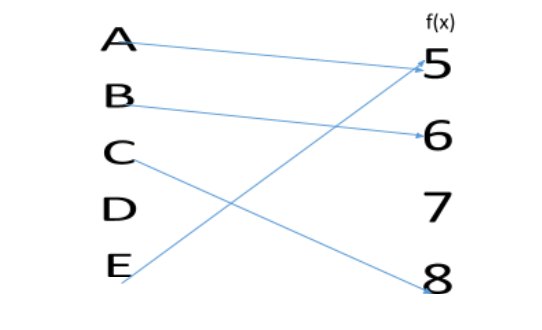
Here, the domain is the set {A,B,C,E}. B is not in the domain, since the function is not defined for B.
The range is the set {6,7,8}. 5 is not in the range, since there is no letter in the domain that mapped with 5.
What is a function?
In simple language Functions are a type of a machine which gives you a different output of your input i.e. we input different numbers and we get new numbers as the result. So, it is the relation between a set of inputs having one output each. Every function has parts known as domain, codomain or range. We generally denote function by f(x) where x is the input. And represents function as y = f(x).
What is the relation?
A Relation is a combination of wanted sets. An arranged pair, normally called a point. A group of pair of input and output values shown in an order.
It is the correspondence between sets and data.
Example: The relationship between favourite subjects of a student and marks scored.
(x,y)= (favourite subject, marks)
SetA = {(maths,98),(english,92),(science,90)}.
Types of Relations in Mathematics
Empty Relation – when there is no relation between sets it is written as R = ∅.
Universal relation – empty and universal relations are known as trivial relations. A universal relation is a relation in which each member is related.
Identity relation – it is a relation in which every element of a set is related to itself.
Inverse relation – if we have a relation between two sets say A and B Then, the inverse relation of R can be written as R-1 = {(b, a) : (a, b) ∈ R}.
Reflexive relation – a relation in which every set of A maps with itself.
All functions are related but not all relations are functions.
What is the range?
After substituting the domain, all the outputs of a function are known as range.
It is the set of all possible resulting values of the dependent variable (y, usually).
They are the coordinates of the y-axis.
What is the domain?
The domain of R is the set of all first elements of the ordered pairs in relation R.
It is a complete set of possible values of the independent variable.
They are the coordinates of x-axis.
The values for the domain should not have 0 in their denominator.
Codomain of a function
It is the set of values that could possibly come out.
It is also on the output side as range but range is the actual value which comes out.
It restricts the output of a function.
It relates to the definition of the function.
Functions and their domain
f(x) = x2 – 2x+5, domain – (-∞, ∞)
f(x)= log (x-7), domain (7, ∞)
How to find the domain of a function?
The set of all real numbers can be used as a domain.
Some exceptional cases are: a) The domain will be the set of all real numbers when the form of given function is f(x) = 3x + 6 or f(x) = x2 – 6.
- b) If the set of given functions is f(x) = 1/(x – 1), then accept 1 the set of all real numbers will be domain.
Domains are restricted for not defined functions.
Domain of logarithmic function is x>0
Domain and range of trigonometric functions.
Let us take first trigonometric identity i.e. sin²x + cos²x = 1
We can write it as cos²x = 1 – sin²x
cosx = 1-sin2x
As the cosine function is defined only for real values therefore the value inside root should be positive.
1 – sin²x ≥ 0, sin x ∈ −1,1.
Domain of sin (x) is all real numbers.
Therefore, the domain for the trigonometric functions f(x) = sin x and f(x) = cos x will contain the entire set of real numbers. And represented as
-1 ≤ sin x ≤1
-1 ≤ cos x ≤1
Domain, range and function for f(x)= tan x
We know that,
tan x = sin x / cos x
tan x will be defined for all values except the values where cos x = 0.
( because denominator of domain can’t be 0)
cos x is zero for the angles π/2, 3 π/2, 5 π/2 etc.
cos x = 0 ∀ ∈(2n+1)/2 , where n ∈ z.
tan is not defined for these values
so, the domain for tanx = R-(2n+1)/2 , Range= all real numbers.
Conclusion
The domain and range of function constitutes all possible inputs and outputs of a function respectively. We can find the domain and range of a function algebraically or graphically. Domains are usually coordinates of x- axis and range are coordinates of y-axis. You will find a domain in all real numbers except numbers having denominator 0 or negative sign in root. tan x will not be defined for all those values where cos x is 0 because we know that tan x = sin x / cos x And denominator should not equal 0.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



