To distribute something is to split it or to give someone a piece or a portion of it. As per distributive property, multiplying the sum of two or more addends by a number yields the same result as multiplying each addend by the number individually and then putting the products together.
The way total output, income, or wealth is allocated among individuals or among the factors of production is known as distribution in economics (such as labour, land, and capital). Each unit of production corresponds to a unit of income in general theory and, for example, in the United States’ National Income and Product Accounts. National accounts are used to classify factor incomes and measure their proportions in the same way as national income is. Adjustments to the national accounts or other data sources are typically utilised when the focus is on individual or household income. The fraction of income flowing to the top (or bottom) x percent of households, the next x percent, and so on (defined by evenly spaced cut points, say quintiles) is typically of importance here, as are the factors that may alter them (globalization, tax policy, technology, etc.).
Distribution
One of the four elements of the marketing mix is distribution (or location). The practice of making a product or service available to the consumer or business user who requires it is known as distribution. Developing a well-coordinated distribution strategy is a part of strategic planning. At the strategic level, there are three basic distribution approaches: mass, selective, and exclusive. The quantity and type of intermediaries chosen are largely determined by the strategy. The general dissatisfaction
Distribution Formula
Cumulation Distribution Function
You can compute the likelihood of an occurrence using the probability density function (PDF) of a random variable, X, as follows:
- The likelihood that X has values in the interval (a, b) for continuous distributions is equal to the area under its PDF in the interval (a, b).
- The probability that X has values in the interval (a, b) for discrete distributions is equal to the sum of the PDF (also known as the probability mass function) of the potential discrete values of X in the interval (a, b) (a, b).
Determine the probability density function’s value at a known value x of the random variable X using PDF.

Inverse Cumulative Probability
The inverse cumulative distribution function (ICDF) of a random variable X determines, when possible, a value x such that the probability of X x is greater than or equal to p for an integer p in the closed interval [0,1].

Beta Distribution
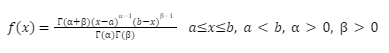
Distribution Meaning
The term “distribution” refers to the act of spreading a product over a marketplace so that it can be purchased by a wide number of individuals.
- A good transportation system for getting commodities to different parts of the country.
- An effective tracking system to ensure that the correct goods arrive at the correct time and in the correct quantity.
- Good packaging that can withstand the rigours of transportation.
- Tracking the locations where the product can be placed so that the largest number of people can see it and buy it.
- It also includes a system for recovering products from trade.
Conclusion
A company’s distribution can make or break it. Simply said, a robust distribution system means that the company has a better chance of selling more of its items than its competitors. Greater margins absorb raw material price increases better and survive longer in challenging market conditions for the company that spreads its products wider and faster into the market place at cheaper prices than its competitors. Any industry or service relies heavily on distribution. If the product is not available for purchase at the points where consumers can acquire it, the best pricing, promotion, and people are all for naught.
Companies in India’s FMCG industry, in particular, distribute low-value, high-volume products to nearly 1 million retail locations, or points of sale. Factory, stock points, distributors or C&F (carrying and forwarding agencies), wholesalers, retailers, and customers are all part of the most successful FMCG companies’ networks. Even direct marketing is now seen as a viable distribution channel.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






