Calculus is one of the most significant branches of mathematics since it deals with continuous change. The fundamental principles of calculus are derivatives and integrals. The area under the curve of a function is measured by its integral, whereas the rate of change of a function is measured by its derivative. The integral gathers a function’s discrete values over a range of values, whereas the derivative gives the function’s explanation at a specific point. Calculus is also known as infinite calculus or “the calculus of infinitesimals.” The study of continuously changing functions is known as classical calculus.
Calculus is a mathematical concept that is commonly utilized in mathematical models to get optimal solutions and so aids in understanding the changes in the values associated with a function. Calculus is divided into two sections: the first is called differential calculus and the second is called integral calculus.
- Differential calculus
- Integral calculus
Differentiation and integration are two of the most significant branches of calculus, and the differentiation and integration formulas are interchangeable. The outcome of integrating the derivative of a function is the original function. To put it another way, integration is the inverse of differentiation, which is why an integral is also known as the antiderivative. Differentiation is used to break down a function into components, while integration is used to put those components back together to form the original function. The differentiation and integration formulas are used in geometry to compute the slope and area under a curve, respectively. Differentiation and integration are calculus branches in which the derivative and integral of a function are determined. Differentiation is the process of determining the relationship between a slight change in one variable and a tiny change in another quantity that is reliant on the first. Integration, on the other hand, is the process of determining the area under a function’s curve. We can determine a function’s differentiation and integration at certain values and within a finite range of finite limitations. Definite integration is the process of integrating a function within a determined and finite set of limits.
The fundamental formula for differentiating and integrating a function f(x) at a point x = a is,
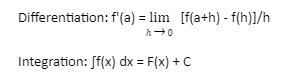
Formulas for Differentiation and Integration
When you differentiate a function f(x), you get f'(x), which is its derivative, and when you integrate f'(x), you get the original function f. (x). In some cases, the reverse process of integration is unable to generate the original function’s constant terms, hence the constant “C” is added to the integration results.
Difference Between Differentiation and Integration
Let’s look at the distinctions between differentiation and integration now that we’ve grasped the concept of differentiation and integration. Below mentioned their distinctions as well as the significant differentiation and integration aspects.
- Differentiation is the process of calculating a quantity’s rate of change in relation to another quantity, whereas Integration is the process of combining smaller components into a single unit that functions as a single component.
- Integration is used to obtain the area under the curve of a function that is integrated, whereas differentiation is used to get the slope of a function at a point.
- Derivatives are examined at a single point, whereas Definite Integrals of Functions are examined over a range of values.
Similarities in Differentiation and Integration
Following that, we’ll go through some of differentiation and integration’s shared features and commonalities. Both differentiation and integration satisfy the following commonalities and common formulas:
1- They meet the linearity property, i.e.(f(x) ± g(x))/dx = d(f(x))/dx ± d(g(x))/dx and ∫[f(x) ± g(x)] dx = ∫f(x) dx ± ∫g(x) dx
2-Differentiation and integration are mutually exclusive processes.
They meet the scalar multiplication property, with d(kf(x))/dx = kd(f(x))/dx and ∫kf(x) dx = k ∫f(x) dx, respectively.
Important reminders to Keep in Mind About Differentiation and Integration:
The processes of differentiation and integration are polar opposites of one another. As a result, when we integrate the derivative of a function, we obtain the original function as well as the integration constant.
A small rate of change in a quantity is achieved by differentiation. Integration, on the other hand, delivers a value over continuous limits and describes the function’s cumulative effect.
Conclusion:
Differentiation is the algebraic method for calculating derivatives. The derivative of a function is the slope or gradient of a certain graph at any given place. The gradient of a curve is the value of the tangent traced to it at every given point. For non-linear curves, the gradient varies at different points along the axis. As a result, determining the gradient in these circumstances is difficult. It’s also known as a property’s change in relation to the unit change of another property.
Integration is the process of calculating definite or indefinite integrals. For some function f and a closed interval [a, b] on the real line (x).
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






