When a cone is cut at different angles, the edge of the cone marks different curves. These curves are frequently referred to as conic sections. A conic section is a curve formed by crossing a right circular conic surface and a plane surface. Different conic sections are given at various intersection angles.
More About Ellipse
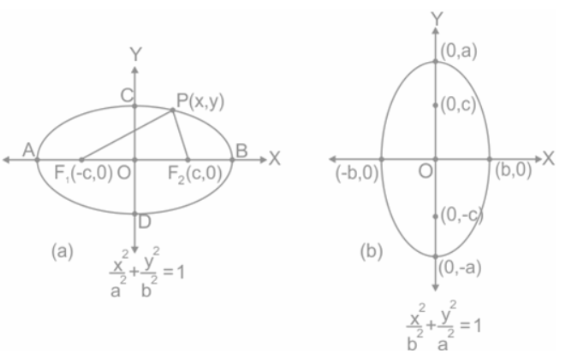
The ellipse is one among the conic sections that’s produced, when a plane cuts the cone at an angle with the bottom. All circles are a particular case of the ellipse since the definition of an ellipse entails being parallel to the cone’s base. Ellipses have the following characteristics:
- Ellipse has two focal points, which are called foci.
- The fixed distance parallel to the latus rectum and perpendicular to the major axis is termed the directrix.
- The eccentricity of the ellipse lies between 0 and 1. 0 ≤ e < 1
- The total sum of each distance from the locus of an ellipse to the two focal points is constant.
- Ellipse has one major axis and one minor axis and a centre.
The Standard form of equation of ellipse is
(x-h)² / a² + (y-k)² / b² = 1
More About Hyperbola
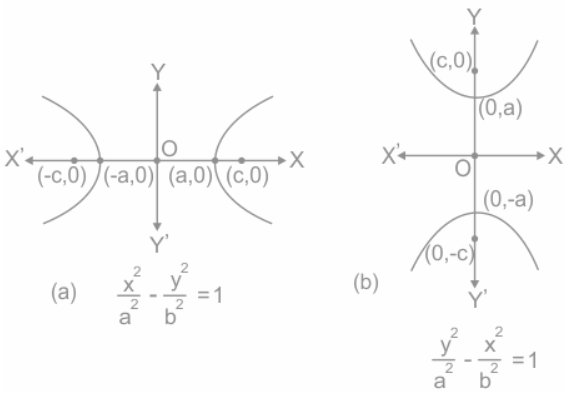
When a plane is parallel to the central axis of a cone, it touches both halves of the double cone, forming a hyperbola. Hyperbolas have two branches as well as the following characteristics:
- Asymptote lines are two linear graphs that the hyperbola’s curve approaches but never touches.
- The intersection of the asymptotes forms a centre.
- Each of the two branches bends around two focal points.
- Each branch has two vertices.
The Standard form of equation of Hyperbola is
(x-h)² / a² – (y-k)² / b² = 1
A hyperbola’s eccentricity is constrained to e > 1 and has no upper bound. When the eccentricity is allowed to reach +∞, the hyperbola degenerates into a straight line, which is one of its degenerate examples. A hyperbola’s other degenerate situation is to become its two straight-line asymptotes. When the plane intersects the apex of the double cone, this occurs.
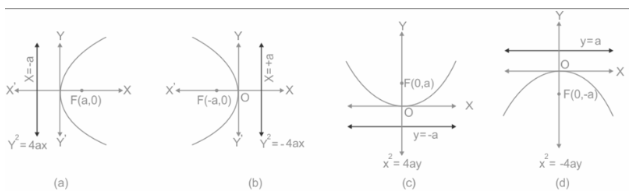
More About Parabola
When the plane is parallel to the cone’s surface, the plane forms a U-shaped curve. The following characteristics can be found in every parabola:
- The curve turns around at a point called Vertex, it is on the curve.
- The point which is not on the curve about which the curve bends, is called the Focus.
- A line connecting the vertex and focus is known as the axis of symmetry, which divides the parabola into two equal halves.
The eccentricity value e = 1 is shared by all parabolas. Because all parabolas have the same eccentricity, they are all similar, which means that any parabola may be turned into another by changing its position and scaling. A parabola degenerates when the plane barely touches the outside surface of the cone, indicating that it is tangent to the cone. Out of the cone’s diagonal, a straight-line intersection result. Non-degenerate Parabolas can be represented using quadratic equations. Eg: f(x)=x2.
Difference Between Hyperbola and Ellipse
At a single glance the equations of both ellipse and hyperbola look similar but the properties of them are completely different.
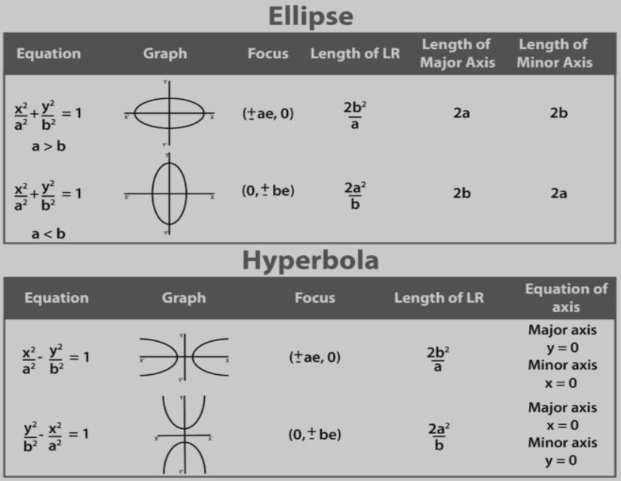
- Both ellipse and hyperbola are symmetrical about their main and minor axes, but the position of the directrix varies. It is outside the semi-major axis in the ellipse but inside the semi-major axis in the hyperbola.
- The perpendicular bisector of the major axis intersects the ellipse but does not intercept the hyperbola.
- Ellipse is a closed curve and the hyperbola is an open curve.
- Ellipse has finite perimeter whereas the hyperbola has infinite length
Conclusion
A ‘conic’ curve is one that is created by crossing a right circular cone with a plane. Euclidean geometry possesses unique features. The vertex of the cone separates the conic section into two nappes, the upper nappe and the lower nappe. A conic section is a locus of a point P travelling in the plane of a fixed point F known as focus and a fixed line d known as directrix (with the focus not on d) in such a way that the ratio of point P’s distance from focus F to its distance from d is a constant e known as eccentricity.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






