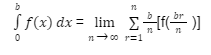The definite integral of any function can be written as the limit of a sum, or as the difference of the values at points a and b if an antiderivative F exists for the interval [a, b]. The total of an endlessly large number of rectangles with infinitesimally small widths is the area under the curve. In the limit where their number approaches infinity, these rectangles precisely give the area under the curve.
Limit of sum
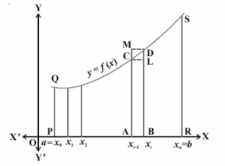
Consider a curve that extends over the x-axis. This graph’s function is a continuous function defined on the closed interval [a, b], with all of the function’s values being non-negative. The definite integral afb(x) dx. Any such continuous function ‘f’ is the area bound between the curve, the points ‘x = a’ and ‘x = b’, and the x-axis.
Take a look at the graph below:
Let’s look at the area PRSQP between the curve y = f(x), the x-axis, and the coordinates ‘x = a’ and ‘x = b’ to see how this works. Divide the interval [a, b] into n equal subintervals, as follows:
[x0, x1], [x1, x2], [x2, x3] …. [xn – 1, xn], where,
x0 = a, x1 = a + h, x2 = a + 2h, x3 = a + 3h ….. xr = a + rh and xn = b = a + nh
Or, n = (b – a)/h. Note that as n → ∞, h → 0.
Now, the PRSQP area in question is the total of all the ‘n’ sub-regions, with each sub-region specified on subintervals [xr – 1, xr], r = 1, 2, 3… n. Examine the region ABDM in the diagram above. The following observation can be made:
A rectangle’s area (ABDM) > A region’s area (ABDCA) > A rectangle’s area (ABLC)
Let this be Equation (1)
Also observe that as h 0 or xr – xr-1 0 ( i.e., approaches zero), all three regions become nearly equal. As a result, we’ve
h [f(x0) + f(x1 ) + f(x2) + …. f(xn-1)] = hr=0∑n–1 f(xr) = sn
Let this be equation (2) and
h [f(x1 ) + f(x2) + f(x3) + …. f(xn)] = hr=1∑n f(xr) = Sn
Let this be equation (3)
For r = 1, 2, 3,…, n, sn and Sn signify the sum of areas of all lower rectangles and upper rectangles raised over subintervals [xr–1 , xr]. To put it in context, equation (1) can be rewritten as follows:
Sn > area of the region (PRSQP) > sn
These strips become narrower as n increases.
Furthermore, it is assumed that the limiting values of (2) and (3) are the same in both circumstances, and that the required area under the curve is the common limiting value. We have, symbolically,
limn∞ Sn = limn∞ sn = area of the region (PRSQP) = afb(x).dx
Let this be the equation (4)
This area also serves as the limiting value for any region that lies between the rectangles below the curve and the rectangles above the curve. We’ll use rectangles with the same height as the curve at the left-hand edge of each sub-interval for ease. Equation 5 is thus rewritten as:
afb(x).dx = limn∞ h[ f(a) + f(a+h) + … + f(a+(n-1)h)]
afb(x).dx = ( b – a ) limn∞ (1/n)h[ f(a) + f(a+h) + … + f(a+(n-1)h)]
where, h=b-an/0 as n
Let this be called equation (5)
Definite Integral is defined as the limit of a sum in this equation.
Note: The value of a function’s definite integral over any given interval is determined by the function and the interval, but not by the integration variable used to represent the independent variable. As a result, the integration variable is referred to as a dummy variable.
Conclusion
The total of an endlessly large number of rectangles with infinitesimally small widths is the area under the curve. In the limit where their number approaches infinity, these rectangles precisely give the area under the curve.
here, h is (b-a)/n,
It’s worth noting that if a the lower limit is zero, then
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out