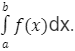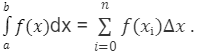The definite integral is the area below the curve between the two fixed limits. For the function f (x) defined for the x-axis, the definite integral is expressed as
Where a is the lower limit and b is the upper limit. Divide the area into rectangles and add them together to find the area below the curve between the two boundaries. The area will be more realistic if there are more rectangles. Therefore, divide the area into an infinite number of rectangles, each of the same (very small) size, and sum all the areas. This is the basic theory behind definite integrals.
The integral is the sum of the areas, and the definite integral is used to find the area within the boundary. Integration was first studied in the 3rd century BC. Used to find areas of circles, parabolas, and ellipses. Learn more about definite integrals and the properties of integrals.
Formula of Definite integral
Given a continuous function f (x) in the interval [a, b], divide the interval into n subintervals of equal width Δx and select points from each interval x ∗ i. In that case, the definite integral of (x) goes from a to b is
Geometrical Interpretation of the Definite Integral
In general, ∫ba f(x) dx represents the algebraic sum of the curves y = f (x), the x-axis, and the straight lines x = a and x = b. Areas above the x-axis are marked with a plus sign, and areas below the x-axis are marked with a minus sign. ∫ba (x) dx region OLA – region AQM – region MRB + region BSCD
Note: ∫ba f(x) dx represents the algebraic sum of the regions, where the region of the function y = f is between (x) a and b. Is queried.
=> Boundary area = ∫ba | f (x) | dx, not represented by ∫baf(x) dx
The Definite Integral as a Sum Limit
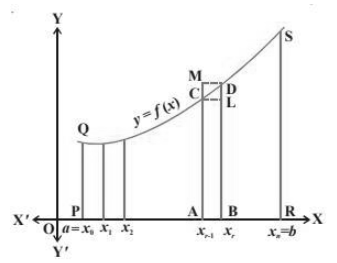
Consider a curve that extends over the x-axis. The characteristic of this graph is a non-stop characteristic described on a closed interval [a, b], in which all of the values of the characteristic are non-negative. The location of the curve, the points ‘x’ = ‘a’ and ‘x’ = ‘b’ and the x-axis is the specific integral ∫ab f(x) dx of such a non-stop characteristic ‘f’.
To understand this, we evaluate the area PRSQP between the curve y = f (x), x-axis and the coordinates “x = a ” and “x = b”. Now divide the interval [a, b] into “n” equal subintervals as shown below.
[x0, x1], [x1, x2], [x2, x3] …. [xn – 1, xn], where,
x0 = a, x1 = a + h, x2 = a + 2h, x3 = a + 3h ….. xr = a + rh and xn = b = a + nh
Or, n = (b – a)/h. Note that as n → ∞, h → 0.
The area PRSQP considered here is the sum of all “n” sub-areas. Each sub-region is defined by the sub-spacing [xr – 1, xr], r = 1, 2, 3… n. Next, consider the area. ABDM in the figure above. You can make the following observations:
Rectangle area (ABLC) & let; Area (ABDCA) & let; Rectangle area (ABDM) ……. (1)
Also, as h → 0 or xr – xr – 1 → 0, all three areas are almost equal. Please note that it will be. Therefore,
sn = h [f (x0) + f (x1) + f (x2) +…. f (xn – 1)] = h r = 0∑n–1 f (xr)… (2)
And Sn = h [f (x1) + f (x2) + f (x3) +…. f (xn)] = h r=1∑n f (xr)… (3)
Where sn and Sn are the sum of the areas of all the lower and upper rectangles that occur in the subinterval [xr – 1, xr] when r = 1, 2, 3…, n. In overview, equation (1) can be rewritten as:
sn & lt; Area of area (PRSQP) & lt; Sn… (4)
CONCLUSION
The definite integral of a function is closely related to the indefinite and indefinite integrals of a function. The main difference is that if you have an infinite integral, it’s a real value, while the latter two represent an infinite number of functions that differ only in constants. The relationship between these concepts is explained in the section on the fundamental theorem of calculus, and we can see that definite integrals apply to many problems with calculus.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out