Introduction
The cosine function (cos) is a mathematical function that connects a triangle’s interior angle to the length of its sides. The cosine function is one of the three basic trigonometric functions, along with the sine and tangent functions. The cosine of an angle in a right triangle is equal to the ratio of the side nearest to the angle to the length of the right triangle’s hypotenuse. In terms of math, this is:
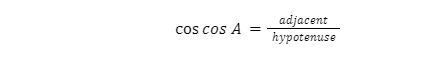
Angle measurements are passed to the cosine function, which provides a ratio as an output. When
A=00, the cosine function has the following value.
Cos 0 degrees has a value of 1. The equivalent of the given angle (0 degrees) in radians can similarly be used to express Cos 0 degrees.
Using the degree to radian conversion, θ we know that in radians = θ in degrees (pi/180°).
0 degrees = 00× (π/180°) rad = 0π or 0 .
cos 00= cos(0) = 1
cos(0) = 1
A zero-degree angle’s cosine is equal to one. Consider what happens to a right triangle when one of its angles approaches zero. The opposite side gets smaller and smaller as the angle approaches zero. The lengths of the hypotenuse and side adjacent to the angle increase closer and closer as the angle gets smaller. The hypotenuse and adjacent side will fit perfectly on top of each other once the angle measurement reaches zero, forming a 1-to-1 ratio. As a result, the cosine of 0 equals 1.
Identities of cos 0°
To represent cos 0°, we can utilize trigonometric identities such,
–

The cosine of angle zero degrees can be calculated using three different mathematical procedures, two of which are linked to geometric systems and the other to trigonometry.
Fundamental method
We use a property between the sides of a triangle to prove the exact value of the cosine of angle zero degrees in this manner. Consider a right triangle with a zero-degree angle. Here’s an illustration of a right triangle with a zero angle.
The Triangle QPR is an example of a right triangle with a zero degree angle.
Express the cos function in ratio form in terms of side lengths, as defined by the definition.
When the angle of a right triangle is zero radian, the cos function is represented as cos 0


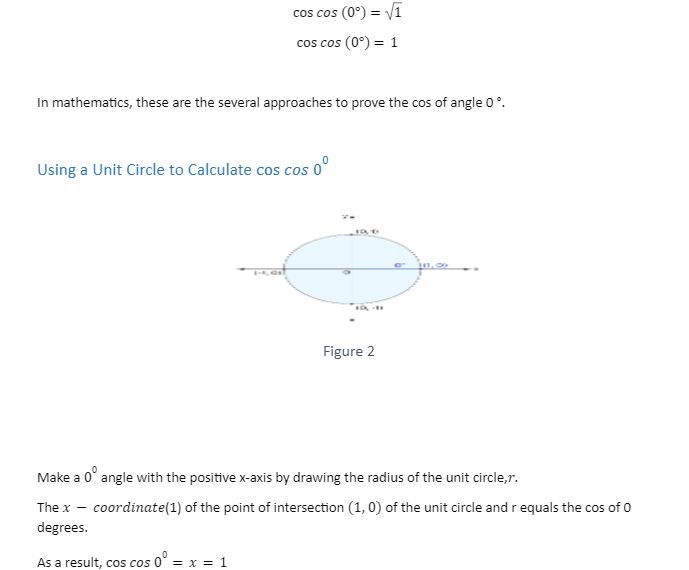
Conclusion
In this article, we study that trigonometry, the cosine function, is a periodic function that is particularly essential. The unit circle is the simplest method to comprehend the cosine function. Draw a unit circle on the coordinate plane and draw the angle centered at the origin , with one side as the positive x-axis, for a specified angle measure. The secant of any angle x for which cos x=0, should be unknown since the denominator would be zero because secant is the reciprocal of cosine. Because cos (pi/2) has a value of 0, the secant of (pi)/2 must be undefined.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






