⁄The point of tangency is the point of intersection of the circle and its tangent. The tangent is parallel to the circle’s radius, with which it intersects. Any curved form can be termed a tangent. Because tangent is a line, it has its own equation.
A tangent of a circle is the line that intersects the circle only at one point. At each given point, there can only be one tangent. The point of tangency is the point at which the tangent intersects the circle.
Tangents and normal:
The lines linked with the curve are tangents and normals. A tangent, or a line that intersects the curve at a certain point, exists for each point on the curve. The normal line is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact.Tangent equation for the point (x1, y1) is (y – y1) = m(x – x1), whereas the equation for a normal travelling through the same place is (y – y1) = -1/m (x – x1).
Tangent Circle Formula:-
In geometry, a tangent of a circle is a straight line that only touches the circle at one point. A tangent never penetrates the interior of the circle.
The tangent has two key characteristics:
At one point on a circle, a tangent intersects it.
The tangent makes a right angle at the point of contact with the radius/diameter of the circle.
Let’s take a look at the tangent equation now. A tangent is a line, and we need two things to write its equation:
Slope (m)
A point on the line
These were the general equation of the tangent to the circle:
For a line y = mx +c, the tangent to a circle equation x2+ y2= a2 is provided by the equation
The equation of tangent to a circle x2+ y2= a2 at (a1 , b1) is xa1 + yb1 = a²
As a result, the tangent equation can be written as xa1+yb1 = a2, where (a1 , b1) are the coordinates used to create the tangent.
Point of tangency:-
A tangent is aline that touches a curve(say for example circle),at only one point. The tangent only comes into contact with the curve once. The tangent does not pass through (intersect) the curve.
Point if tangency of circle:-
If more than one line ‘balances’ on a single circle, it can have many points of tangency. When a square is placed around a circle, each side of the square has a point of tangency on the circle.
A, B, C, and D are all points of tangency on the above drawn circle.
Condition of tangency of hyperbola:-
Tangents in various forms for hyperbolas are discussed in this section.
In our discussion, we shall use the hyperbola x2 /a2-y2/b2=1
Consider the given hyperbola’s point P(x1,y1). Differentiating the equation of the hyperbola yields the slope of the tangent at this point.
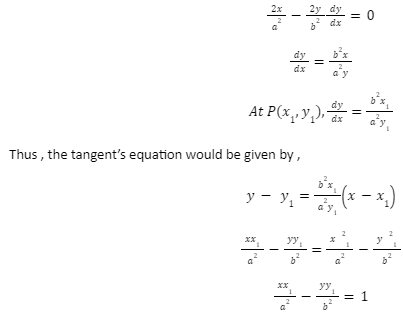
Condition of tangency of ellipse:-
A plane curve that surrounds the two focus points and keeps the total distances to the focal point constant at each point on the curve. A circle is an unique sort of ellipse in which both focus points are located at the same position. A tangent to the ellipse is a line that intersects the ellipse at a point.
If the line y = mx + c contacts the circlex2a2+y2b2= 1,then, c² = a²m² + b².The tangents to the ellipse are represented by the straight liney = mx ± [a2m2+ b2].
Conclusion:-
A line touching circles or an ellipse at only one point is known as the tangent of a circle. When a line contacts the curve at P, this point “P” is referred to as the point of tangency.
A tangent is a horizontal line on a curve that contacts the curve’s point and has the same slope as the gradient or derivative. At any point in the definition, one can deduce how to get the tangent’s equation.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






