It is well understood that two non-parallel lines cross at one location. Concurrent lines are generated when two straight lines cross at one common point or if a third line is formed going through one common point. The term “concurrent” refers to something that happens at the same time or at the same location.
When three or more lines cross through or coincide exactly at one common point, they are referred to as concurrent. The point of concurrency is the common place where all the lines cross or coincide.
According to Eculid’s Lemma, two lines can only have one common point of intersection. Concurrent lines are defined as three or more lines that meet perfectly at one single point in a plane. The point of concurrency is defined as the intersection of three or more lines.
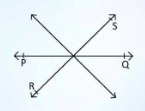
A few examples include a circle’s diameter and its centre. The line segments connecting the midpoints of opposite sides and the diagonals are contemporaneous in quadrilaterals. The three lines in the diagram below intersect at point P. All three lines are running at the same time.
Concurrent Lines of a Triangle
A triangle is a two-dimensional shape with three sides and angles. If line segments are drawn inside a triangle, there can be concurrent lines. Regardless of the triangle’s type, there are four different concurrency points. These are the four points:
Incenter
Inside a triangle, this is the place where the three angular bisectors (lines separating the angles into two equal portions) intersect.
Circumcenter
Inside a triangle, this is the place where three perpendicular bisectors (lines that divide a given line into two equal pieces at right angles) connect.
Centroid
This is the place where the three medians (lines connecting the vertex to the opposite side’s midpoint) of a triangle meet.
Orthocentre
This is the place where the three heights (perpendicular lines from the vertex to the opposing side) of a triangle meet.
Difference Between Concurrent Lines and Intersecting Lines
As we all know, when three or more lines, line segments, or rays intersect at a common point, they are said to be in concurrency. In the case of intersecting lines, however, there are only two lines, line segments, or rays that meet at a single place.
In tabular form, some differences between concurrent and intersecting lines are shown below.
Concurrent lines | Interesting lines |
A single point is crossed by three or more lines. | There are only two lines that cross each other. |
A point of concurrency is the sole point where these lines cross each other. | The point of intersection is defined as the junction of two lines. |
Concurrent Line Segments and Rays
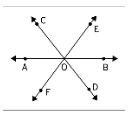
Concurrent line segments are defined as three or more line segments intersecting at one single place. AB, CD, and EF are three line segments that intersect at point O in the diagram below. As a result, it is possible to apply concurrency to line segments.
Concurrent rays occur when three or more rays in a two-dimensional plane intersect at the same spot. The point of concurrency for all rays is defined as the commonplace where all of the rays meet. Three rays PQ, RS, and MN that meet at point O are shown to be contemporaneous in the diagram below.
Point of Concurrency
Concurrent lines are defined as three or more lines passing through the same place. The point of concurrency is the point where all the lines meet or intersect. For example, if lines A, B, and C are concurrent lines that meet at a location Z, then Z is the point of concurrency where the three lines intersect.
Conclusion
If two lines in a plane or higher-dimensional space intersect at a single point, they are said to be contemporaneous. They are the polar opposite of parallel lines. Concurrent lines are generated when two straight lines cross at one common point or if a third line is formed going through one common point. The point of concurrency is the common place where all the lines cross or coincide.
According to Eculid’s Lemma, two lines can only have one common point of intersection. Concurrent lines are defined as three or more lines that meet perfectly at one single point in a plane. The point of concurrency is defined as the intersection of three or more lines.
A few examples include a circle’s diameter and its centre. The line segments connecting the midpoints of opposite sides and the diagonals are contemporaneous in quadrilaterals, etc.
As we all know, when three or more lines, line segments, or rays intersect at a common point, they are said to be in concurrency. In the case of intersecting lines, however, there are only two lines, line segments, or rays that meet at a single place.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out