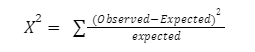A statistical approach for determining the difference between observed and predicted data is the Chi-Square test. This test can also be performed to see if it corresponds with our data’s categorical variables. It can be used to determine whether a discrepancy between two category variables is due to chance or is the result of a relationship.
The observations are divided into mutually exclusive types in normal uses of this test. The test statistic generated from the observations follows a X2 frequency distribution if the null hypothesis states that there are no differences in the population between the classes. The test’s goal is to determine how likely the observed frequencies are if the null hypothesis is correct.
Purpose of a chi-square test
Chi-square is a statistical test that examines the differences between categorical variables from a random sample in order to determine if the expected and actual results are well-fitting.
Chi square test formula
The number of variables that can change in a statistical calculation is represented by degrees of freedom. To verify that chi-square tests are statistically valid, the degrees of freedom can be determined. These tests are widely used to compare observed data with data that would be predicted if a certain hypothesis were correct.
Degrees of Freedom: The number of degrees of freedom does not necessitate any complicated computations. To reduce the number of levels in our category variable, simply subtract one. We’ll use this number to determine which of the infinite chi-square distributions to use.
The observed values are those that you have gathered on your own.
Based on the null hypothesis, the predicted values are the expected values.
Chi Square Formula Applications
- Biologists use it to see if two variables have a significant relationship, such as the relationship between two species in a community.
- Genetic analysts use this to interpret the numbers in different phenotypic classes.
- Used in a variety of statistical procedures to help determine whether to accept or reject a hypothesis
Chi-square test p-value
We produced a chi-square statistic that corresponds to a specific point on a chi-square distribution with the proper amount of degrees of freedom. If the null hypothesis is true, the p-value determines the likelihood of getting a test statistic this extreme. The p-value of our hypothesis test can be calculated using a table of values for a chi-square distribution. If we have statistical software, we can utilize it to get a more accurate estimate of the p-value.
Chi-square test p-value interpretation
The p-value in a chi-square analysis is the probability of getting a chi-square as large as or larger than that in the current trial while still having the data support the hypothesis. It’s the likelihood that variations from the expected are due to chance.
When Should a Chi-Square Test Be Used?
A chi-square test is used to see if observed results match expected results and to rule out the possibility that observations are random. When the data being studied is from a random sample and the variable in question is a categorical variable, a chi-square test is applicable. A categorical variable includes options such as automobile kind, race, educational achievement, male vs. female, and how much someone likes a political candidate among others.
Chi square test vs f test
Difference between Chi square test vs f test given below-
- The Chi-square test determines the best fit of the combination of independent variables to the dependent variable, whereas the F-test determines the best fit of the combination of independent variables to the dependent variable. If you conduct a stepwise regression and choose a coefficient above standard error for each combination, the highest of these will be the optimum combination.
- The Chi-square test is used to compare population variance to a predetermined value, assess the goodness of fit of a probability distribution, and determine if two qualities are independent. The F-test is used to compare two variances from distinct populations and to compare many means using the ANOVA technique.
P-Value in Chi-square
The p-value in a chi-square analysis is the probability of getting a chi-square as large as or larger than that in the current trial while still having the data support the hypothesis. It’s the likelihood that variations from the expected are due to chance.
Use of chi-square test
By assuming that the null hypothesis is true, the chi-square test is used to determine how likely the observations are. A hypothesis is a possibility that a certain condition or statement is true, which we can test later.
Conclusion
The chi-square test is used to determine whether observed results match expected results and to rule out the possibility of random observations. A chi-square test is appropriate when the data being analyzed is from a random sample and the variable in issue is a categorical variable. Options such as automobile type, race, educational achievement, male vs. female, and how much someone loves a political candidate (from very much to very little) are examples of categorical variables.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out