The term product in mathematics refers to the multiplication of two terms. The Cartesian plane is a two-dimensional coordinate plane produced by the intersection of the x- and y-axes. The origin is where the x-axis and y-axes cross perpendicular to each other.
What is the Cartesian Product?
The ordered product of two non-empty sets is the Cartesian product of sets. In other words, the collection of all ordered pairs as the result of the product of the two non-empty sets is called the Cartesian product.
The cross product of the two non-empty sets P and Q is represented as P x Q, the Cartesian product of P and Q. The ordered pairs (p,q) is such that pP and qQ. Therefore, P Q = {(p,q):pP,qQ}
To understand it better, let’s work with an example. Consider two non-empty sets,
D={d1, d2, d3} and H={h1, h2, h3}.
The product of the two sets will be equal to
DH= {(d1,h1),(d1,h2),(d1,h3),(d2,h1),(d2,h2),(d2,h3),(d3,h1),(d3,h2),(d3,h3)}.
If either of the two sets is a null set, i.e., D= or H=, their product will also be a null set in that case.
Number of Ordered Pair
When the Cartesian product of two non-sets, such as P and Q, is found, the number of ordered pairs that will be received is equal to the product of number of elements in each set individually.
For example, Set P has three elements, while Set Q has five. The number of ordered pairs that will be received equals the product of number of elements in each set individually.
Thus, the number of ordered pairs the Cartesian Product of set P and Q will have is 15(35=15).
Cartesian Product Properties
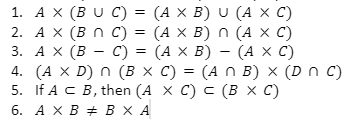
7.(A×B)×C≠A×(B×C)
Theorems Related to Cartesian Product
Theorem 1
For any three different value sets, A, B, and C,

Non-Commutative Property in a Cartesian Product
The Cartesian product of two sets is not commutative, i.e., if there are two sets A and B, then ABBA. This is because when the Cartesian product of sets B and A is done (BA), the ordered pairs are reversed.
The only condition when the product of the two sets can be equal, i.e., (AB) and (BA) can be equal, is when either of the following conditions is fulfilled:
A and B are equal to each other.
A or B or both are empty sets.
To understand the non-commutative property in a Cartesian product, let take an example of three sets,
A = {1, 2}
B = {3, 4}
C = {5, 6}
Then,
AB = {1,2}{3,4} = {(1,3),(1,4),(2,2),(2,4)}
BA ={3,4} {1,2} = {(3,1),(3,2),(4,1),(4,2)}
The Cartesian product of the two sets (AB) and (BA) is not equal. Hence, the Cartesian product is non-commutative.
Non-Associative Property in a Cartesian Product
The Cartesian product of two sets cannot be associative, i.e., if there are three non-empty sets A, B, and C, then (AB)CA(BC). If any of the sets is empty, the product is associative.
Conclusion
The ordered product of two non-empty sets is the Cartesian product of sets. The number of ordered pairs resulting from the product of two sets depends on the number of elements each set has. Cartesian product is always non-commutative and non-associative.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




