Solid shape foundation of solidarity has three roots, which are 1, ω, ω2. Here the roots ω and ω2 are non-existent roots and one root is a square of the other root. The result of the fanciful foundations of the solid shape base of solidarity is equivalent to 1(ω.ω2 = ω3 = 1), and the amount of the block foundations of solidarity is equivalent to zero. (1 + ω + ω2 = 0).
What is Cube Root of Unity?
The 3D shape base of solidarity is addressed as 3√1 furthermore, it has three roots. The three foundations of the 3D square base of solidarity are 1, ω, ω2, which on increase offers the response of solidarity. Among the foundations of the shape base of solidarity, one root is a genuine root, and the other two roots are non-existent roots.
The Cube root of Unity is any number that returns 1 when raised to the third power or multiplied by itself three times. Any number’s cube root is the number that, when raised to the third power, yields the number whose cube root is to be calculated.
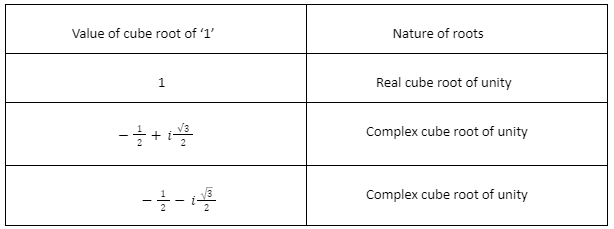
The symbol 3 represents the cube root of an integer. In index form, the cube root is represented by numbers increased to the power 1/3. The cube root of ‘1’ is the cube root of unity. The cube root of unity has three different values. Below are two complex cube roots of unity and one real cube root.
Cube Root of unity Properties
Property 1: The cube root of unity has three different values, one of which is a real root as well as the other 2 are complex cube roots of unity.

Property 2: The square root of one of the unity’s imaginary cube roots is the square root of the other. Let’s look at one of the solutions of the cube root of unity that is complex in nature.
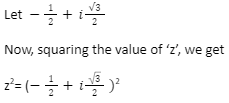
Through using algebraic identity (a + b)²= a²+ b²+ 2ab to solve the expression on the right side of the preceding equation, we get
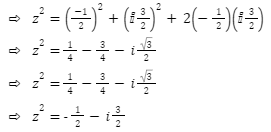
The aforementioned value is another imaginary value of the cube root of unity. One of the imaginary roots of unity is equal to the square of the other hypothetical cube root of unity, according to the proof above.
In general, if one of the imaginary roots is 2, the other is 2. As a result, the roots of unity are likewise written as 1, and 2.
Property 3: A product of two imaginary cube roots of unity equals unity.
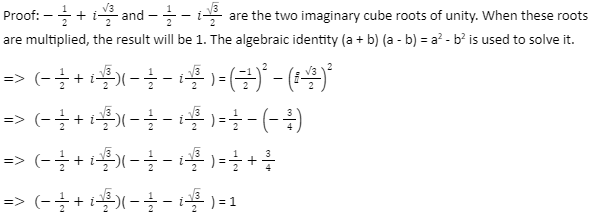
∴ One is equivalent to the product of two imaginary cube roots of unity. The imaginary cube root of unity’s product can also be written as + 2=1.
Property 4: If all 3 cube roots of unity are summed together, the result is zero.
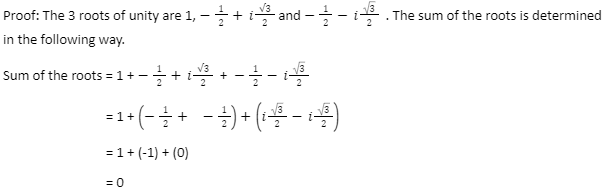
∴ The sum of unity’s cube roots equals zero. 1 + Ѡ + Ѡ2 = 0 is another way to express the sum of the cube root of unity.
Property 5: The imaginary cube root of unity’s cube equals one. ω3= 1
Property 6: The reciprocal of one imaginary cube root equals the reciprocal of the other imaginary cube root.
Proofs: Ѡ3 = Ѡ2.Ѡ = 1
Ѡ = 1/Ѡ and Ѡ2 = 1/Ѡ
Properties of the Cube Root of Unity Fun Facts
- 1, and 2 are the values of the cube root of 1.
- The de Mover number is also known as the cube root of unity.
Conclusion
The cube roots of unity are the numbers that produce the product 1 when multiplied three times or raised to the power of three. Unity’s cube roots are identical to one’s cube roots. Cube roots of unity are used in the number system, complex numbers, factorization, and other areas of mathematics.
A root of unity is just a complex number that equals 11 when multiplied by a positive integer power. Many fields of mathematics are linked to roots of unity, including regular polygon geometry, group theory, & number theory.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




