The digital (logic) circuits are analysed and simplified using Boolean Algebra. It only uses binary numerals, which are 0 and 1. It’s also known as logical algebra or binary algebra. George Boole discovered Boolean algebra in 1854. The scope of Boolean algebra is highly constrained, and any Boolean variable can only have one of two potential values: 1 or 0.
Boolean algebra, rule
The following are some of the most important laws in Boolean algebra.
- Only 2 values are allowed for the variable. Binary 1 indicates HIGH, while Binary 0 denotes LOW.
- An overbar represents a variable’s complement (-). As a result, the complement of variable B is written as B Bar. As a result, if B = 0, B Bar = 1, and if B = 1, B Bar = 0.
- A plus (+) sign between the variables indicates that they are O Red. O Ring A, B, and C, for example, is expressed as A + B + C.
- Writing a dot between two or more variables, such as A.B.C., represents logical ANDing. In some cases, such as ABC, the dot may be omitted.
Boolean Law
Boolean Laws are divided into six categories.
Commutative law: A commutative operation is any binary operation that satisfies the following equation.
A.B=B.A A+B=B+A
The commutative law states that changing the order of the variables has no influence on the logic circuit’s output.
Associative law
The sequence in which the logic operations are conducted is unimportant, according to this law, because their impact is the same.
(A.B.).C = A.(B.C) (A+B) +C = A+ (B+C)
Distributive law
The following condition is stated by distributive law.
A.(B+C)=A.B+A.C
AND law
The AND operation is used in these laws. As a result, they are known as AND laws.
A.0=0 A.A=A A.1=A A.A
OR law
The OR operation is used in these laws. As a result, they are known as OR laws.
A+0=A A+A=A A+1=1 A+A=1
INVERSION law
The NOT operation is used in this law. According to the inversion law, double inversion of a variable results in the original variable.
A̿ = A
Boolean algebra expression
The result of a Boolean expression is always a Boolean value. A Boolean expression is made up of Boolean constants (True or False), Boolean variables, and logical connectives in that order. A Boolean function is represented by each Boolean phrase.
Eg. A Boolean expression is AB’C.
Canonical Forms
There are two types of canonical forms for a Boolean expression:
- The sum of minterms (SOM)
- The Product of maxterms (POM)
The sum of minterms (SOM)
A minterm is the sum of all variables, in either direct or supplemented form. Any Boolean function may be written as the sum of its 1-minterms, while its inverse can be expressed as the sum of its 0-minterms. Hence,
F (list of variables) = ∑ (list of 1-minterm indices)
The product of maxterms (POM)
A maxterm is the sum of all variables, whether they are direct or complemented. Any Boolean function may be written as a product of its 0-maxterms, and its inverse can be written as a product of its 1-maxterms. Hence,
F(list of variables) = π (list of 0-maxterm indices)
Boolean algebra logic
Boolean logic is an algebraic system in which all values are either true or False. True and false values are used to test the conditions on which selection and iteration are based.
For example, A + A equals A, not 2A as in traditional algebra. The basic logic statements that concern us here are given by the logic gate operations of the AND, OR, and NOT gate functions. Boolean Algebra is a simple and effective way of representing the switching action of standard Logic Gates, and the basic logic statements that concern us here are given by the logic gate operations of the AND, OR, and NOT gate functions.
Logic AND Function
The Logic AND Function, function specifies that for an output action to occur, two or more events must occur simultaneously. The order in which these actions take place is immaterial because it has no bearing on the end result. A & B, for example, A & B = B & A. The Logic AND Function in Boolean algebra follows the Commutative Law, which enables a change in the location of either variable.
In electronics, the AND function is represented by the dot or full stop symbol (.) As a result, the output term of a 2-input (A B) AND Gate is represented by the Boolean equation A.B or simply AB.
AND Function Representation as a Switch
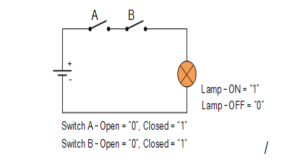 Figure 1
Figure 1
The two switches, A and B, are connected in series to make a circuit. In order to turn on the lamp in the circuit above, both switch A AND switch B must be closed (Logic “1”). To put it another way, both switches must be closed, or at logic “1,” for the lamp to be “ON.”
Then, when “ALL” of its inputs are present, this form of logic gate (an AND Gate) creates an output. Only when all of the inputs are TRUE will the output be TRUE in Boolean algebra. The logic AND function is equivalent to a series circuit in electrical terms, as seen above.
Conclusion
We study, The digital (logic) circuits are analyzed and simplified using Boolean Algebra. It exclusively employs binary digits, namely 0 and 1. It’s also known as logical algebra or binary algebra. The science of probability, set geometry, and information theory all benefit from Boolean algebra. It also serves as the foundation for the design of circuits in electronic digital computers.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






