The term bisector is divided into two parts. First, there’s the prefix ‘bi,’ which we already know stands for two! Second, there’s the root word sector.’ Consider the term sector’ to refer to a section of anything. So, by combining the meanings of the prefix with the base word, we may deduce the meaning of bisector! A bisector is a tool that divides something into two equal parts. We’ll look at two types of bisectors in arithmetic today: the line segment bisector and the angle bisector.
Bisection is the dividing of something into two equal or congruent halves, usually by a line, which is subsequently referred to as a bisector in geometry.
The segment bisector and the angle bisector are the two most common types of bisectors.
Segment bisector:
A segment bisector is a line, ray, or segment that divides a line into two equal halves by cutting another line segment in the middle. The line always bisects or cuts the line segment in half at the middle, separating it into two equal portions. The line can be bisected by one or infinite segments at the midway, and the bisector does not have to be perpendicular.
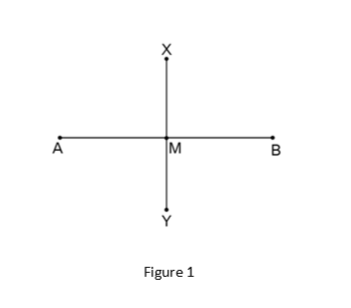
The segment bisector XY divides line AB into two equal halves, AM and MB. A perpendicular bisector is a line that splits a line segment at exactly 90˚. However, because the line does not cut at a perfect angle, in this case, it is referred to as a segment bisector. The midpoint of the line segment AB, where AM = MB, is considered the point M.
To determine whether a line segment is a segment bisector, we can check if it crosses the midpoint, and if it does, we can use the midpoint formula to determine the line’s coordinates. The following is the formula for calculating the midpoint:
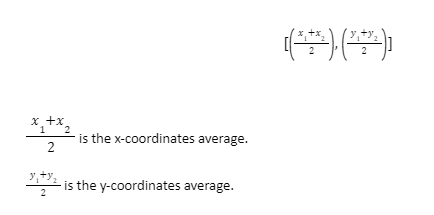
Angle Bisector:
An angle bisector is a ray, segment, or line that divides a given angle into two equal angles. The separation of a single object into two equal halves is referred to as bisectoring or bisection. In geometry, a line or ray is used to split a triangle and an angle, and this is known as an angle bisector.
An angle bisector, for example, will divide a 60-degree angle into two 30-degree angles. It divides one angle into two smaller congruent angles, in other words. An image of ∠AOB’s angle bisector is shown below.
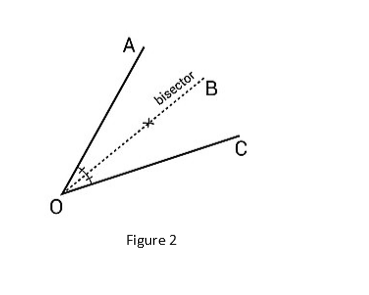
Angle Bisector Properties
The properties of an angle bisector are listed below:
- An angle bisector is a tool that divides a given angle into two equal halves.
- Any point on an angle’s bisector is equidistant from the angle’s sides or arms.
- It divides the opposite side of a triangle into the ratio of the other two sides’ measures.
Bisector length formula
The angle bisector theorem is used to calculate the Bisector length; the formula is detailed below.
Angle Bisector Theorem
The angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths. A triangle’s side is divided into two segments by a line that bisects the opposing angle. It equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the triangle’s other two sides.
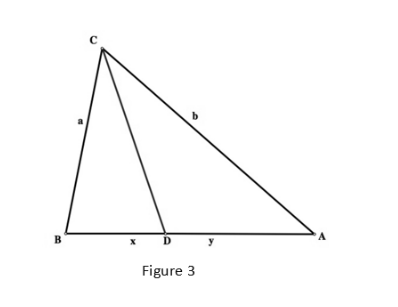
In figure 3, x+y=c(=BA), &l et CD=e is the length of the angle C bisector.
The angle bisector theorem implies, in its most basic form, that
a ⁄ x=b ⁄ y OR ay=bx……….(1)
According to the angle bisector theorem, e, the length of the angle bisector CD, satisfies
e²=ab-xy……..(2)
Proof of theorem
When the sine rule is applied to △BCDand the △ACD and , the result is
a ⁄ sin ∠BDC =x ⁄sin ∠BDC ,b ⁄sin ∠ADC =y ⁄ sin ∠ADC
Using the equality principle sin ∠ADC =sin (π-∠BDC ) = sin ∠BDC & ∠BDC =∠ADC
CD is the angle bisector then, we get
a ⁄ x=sin ∠BDC ⁄ sin ∠BCD =sin ∠ADC ⁄ sin ∠ACD =b ⁄ y
Example of Bisector length formula
Example: XE is the bisector of ∠X. in Δ XYZ. Allow 4 units for XY, 2 units for YE, and 3 units for EZ. Can you figure out how long XZ is?
Solution: Given, XE is ∠X’s bisector.
The angle bisector theorem formula says that
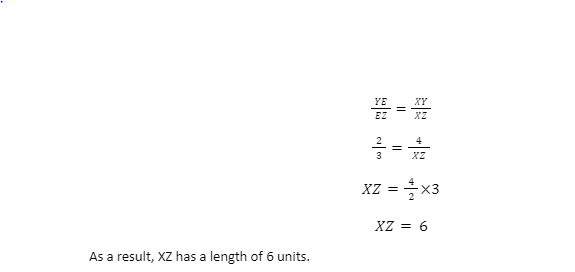
Conclusion
We learned, Bisection is the dividing of something into two equal or congruent halves, usually by a line, which is subsequently referred to as a bisector in geometry. The segment bisector and the angle bisector are the two most common types of bisectors. In locating related sections of similar triangles and solving proofs, bisectors are quite useful. If you draw one of your angle bisectors in a triangle (remember, there are three, one for each vertex), you’ll divide the opposite side correspondingly.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






