The expanded value of an algebraic expression of (x + y)n is determined by using the binomial theorem. It’s simple to calculate the value of (x + y)2, (x + y)3, (a + b + c)2 simply by multiplying the number of times by the integer value. The binomial theorem, on the other hand, may be used to obtain the expanded version of (x + y)17 or other expressions with larger integer values. The binomial theorem expansion’s integer value might be a fraction or a negative integer.
Binomial Theorem
A great Greek mathematician named Euclids originally mentioned the binomial theorem in the 4th century BC. The binomial theorem explains how to extend the algebraic statement (x + y)n to a sum of terms using individual integers of the variables x and y. Each word in a binomial expansion has a coefficient, which is a numerical value.
The binomial theorem states that the nth power of the sum of two integers a and b may be written as the sum of n + 1 terms of the form for every positive integer n.
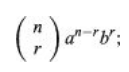
The index r takes on the values 0, 1, 2,…, n in the succession of phrases. The formula defines the coefficients, often known as binomial coefficients.
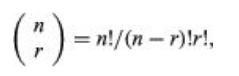
Here n! (also known as the n factorial) is the product of the first n natural integers 1, 2, 3,…, n (where 0! is equal to 1). The coefficients can also be found in what is known as Pascal’s triangle, an array.
The theorem may be used to find permutations, combinations, and probabilities in algebra. Islamic and Chinese mathematicians of the late mediaeval period were aware of the theory for positive integer exponents, n.
Properties of Binomial Expansion
- There are n+1 words in all.
- The first phrase is xn, while the last word is yn.
- As we move from the first to the last phrase, the exponent of x decreases by one. The exponent of y increases by one, whereas the exponent of x increases by one. Furthermore, the sum of both exponents in each phrase equals n.
- By multiplying the coefficient of each part by the exponent of x in that word and dividing the product by the number of that term, we can find the coefficient of the following phrase.
Properties of Binomial Theorem
- Every binomial expansion has one more term than the power of the binomial.
- When the exponents of each term in the expansion are totalled, the result is a sum equal to the binomial power.
- With each subsequent term in the expansion, the powers of the first term in the binomial fall by one, while the powers of the second term grow by one.
- It’s worth noting that the coefficients are symmetrical.
Binomial Theorem for Negative Index
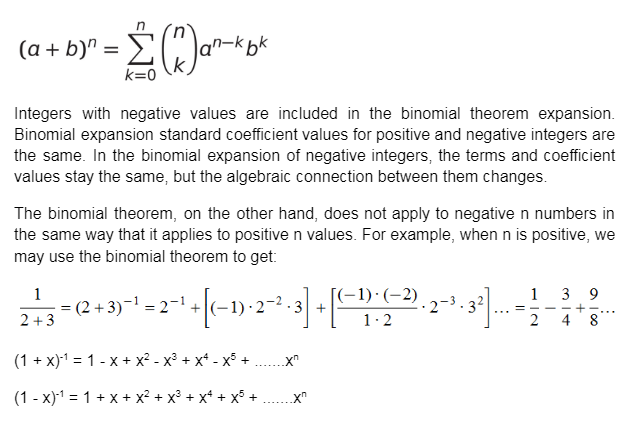
When applying the binomial theorem to negative integers, we first set the upper limit of the sum to infinity; the sum will then only converge under specific conditions. Second, we use complex values of n to extend the definition of the binomial coefficient.
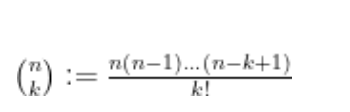
If x is a complex number, then xk is defined for every non-negative integer k — we just multiply twice and define x0 = 1 (even if x = 0). However, unless the value is a positive real, defining a non-integer power of a complex number is difficult.
Conclusion
Now that we have proved the binomial theorem for negative index n, we may deduce that:
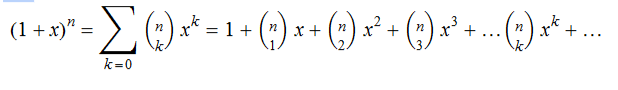
When the condition is true for any integral n, then when n is negative, |x|1
To answer basic mathematics issues, Newton devised the binomial series. Since the binomial series is such a basic mathematical tool, it’s important to have a strong understanding of it so you can utilise it in a variety of scenarios. The above guide is an easy way for you to understand binomial theorem and binomial theorem for negative indexes.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






