An auxiliary circle is a circle of an ellipse mainly determined by the diameter of the major axis and the equation of the ellipse is determined by the variable, i.e., x and y. The equation of a circle is x2+ y2 is equal to a2. Here we will also see one main problem related to the auxiliary circle. Generally, The equation gets formed by dividing the x variable with a and the y variable with b. And both are equal to 1. I.e. x2/a2 + y2/b2 = 1.
Auxiliary Circle
An auxiliary circle is a circle of an ellipse mainly determined by the diameter of the major axis.
- The equation of the ellipse is determined by the variable, i.e., x and y. And the equation of the circle is x2+ y2 is equal to a2.
- The equation gets formed by dividing the x variable with a and the y variable with b.
- And both are equal to 1. I.e. x2/a2 + y2/b2 = 1.
- The oval condition is X2 /a2 + y2/b2 =1; when the significant hub of the oval turns into the measurement of a circle, it is called the helper circle of the oval.
- Here breadth is 2a.
- The span of the circle = a , as focus is at (0,0),
- And the condition of the helper circle of the oval x2/a2 +y2/b2 =1 is x2 +y2 = a2
Director Circle
The chief circle is the locus of the place of the crossing point of sets. And it has opposite digressions to an oval.
Two opposite digressions of circle x2/a2 + y2/b2 are always equal to 1
Whereas y – mx = √(a2m2+b2)
And, my + x = √(a2+b2 m2)
To acquire the locus of the mark of convergence y – mx = √(a2m2+b2) and my + x = √(a2+b2 m2)
mx = √(a2m2+b2) and my + x = √(a2+b2 m2)
, we get
(y – mx)2 + (my + x)2 = (a2m2 + b2) + (a2 + b2m)
⇒ x2 + y2 = a2 + b2, which is the condition of the chief circle.
Auxiliary Circle for a Hyperbola
The Auxiliary circle of a hyperbola has a cross-over pivot as the distance across. The endpoints of the cross-over pivot are the two vertices of the hyperbola, so the circle contains the two vertices of the hyperbola.
The condition of Auxiliary circle adversary a hyperbola is given by x
x2 + y2 = a2
Circle and Ellipse
We will see whether both terms, i.e., ellipse & circle, are different. When we talk about a circle, it is a shut-bent shape that is levelled. All around, the distance is similar from the focal point of the circle.
- A circle is additionally a shut bent shape that is levelled.
- When you include the right ways from two focuses inside the oval (called the foci), they generally amount to a similar number.
- Circles fluctuate in shape from exceptionally wide and levelled to practically roundabout, contingent upon the distance at which the foci are from one another.
- Assuming that the two foci are on a similar spot, the oval is a circle.
Problem-related to Circle
Here we will see some main problems related to the auxiliary circle.
Question: Find the condition to the helper circle of the oval 4x²+ 9y² – 24x – 36y + 36 = 0.
Solution:
4x²+ 9y² – 24x – 36y + 36 = 0
4 (x² – 6x + 9) + 9 (y² – 4y + 4) = 36
(x−3)29+(y−2)24=1.
The oval community is (3, 2)
if the length of the significant hub of the oval be 2a, a² = 9 ⇒ a = 3
x² + y² = a²
x² + y² = 3²
Conclusion
We see that an ellipse is similar to a parabola and hyperbola. The ellipse’s main feature, known as the latus rectum, is the central harmony that is seen opposite to the significant pivot. And the Foci S is always equal to the (ae, 0) and S’ is equal to the (- ae, 0). The equation of an ellipse is determined by the x2 /a2 with the addition of y2 /b2 . These both terms are always equal to the 1 i.e. x2 /a2 + y2 /b2 = 1. The eccentricity always ranges from points 0 and 1

Binomial theorem for positive integral indices
According to the binomial theorem, the total number of terms in an expansion is always more than the index. Take, for example, an expansion of (a + b)n with n+1 terms and n as the index of the equation (a + b)n, where n is any positive integer.
The binomial theorem can be used to extend (x + y)n, where n is any rational number. Let’s look at the binomial theorem for positive integral indices.
The binomial theorem is a rule that can be used to enlarge any power of a binomial.

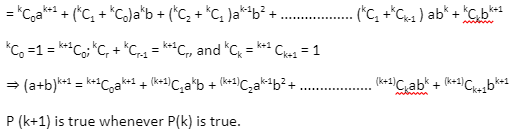
Therefore, P(n) is true for all positive integral values of n.
Properties of binomial theorem
- In the binomial expansion of (x+y)n, the number of coefficients is (n+1).
- In the expansion of (x+y)n, there are (n+1) terms.
- xn and yn are the first term and last term respectively.
- The powers of x decrease from n to 0 as the expansion advances, whereas the powers of y increase from 0 to n.
- The (r +1)th in the general term of of expansion is (x + y) n, which may be written as Tr+1=nCr xn-ryr.
- The coefficients of binomial expansion are organised into Pascal’s triangle.
- The nth term from the end of (x-y)n equals the (n-r+2)th term from the beginning in binomial expansion.
- The middle term in (x + y)n is (n/2)+1 if n is even; however, if n is odd, the middle terms are (n+1)/2 and (n+3)/2.
Coefficient of binomial theorem
The binomial coefficients are the figures associated with the variables x, y, in the expansion of (x +y)n. The binomial portions are represented as nC0, nC1, nC2. The binomial coefficients are attained through the Pascal triangle or by using the combinations formula.
Conclusion
The binomial expansion has more application than algebra II. In statistics, it is used to calculate the binomial distribution.
This allows statisticians to quantify the risk of a certain number of positive results in a set of trials.
Binomial expansion is also intriguing from a fine perspective as it allows mathematicians to gain insight into the properties of polynomials.
Binomial developments are used in numerous numerical and logical calculations, including kinematic and gravitational time enlargement, active energy, electric quadrupole post and determining the relativity factor gamma, to mention a few.
The number of terms in a binomial expansion of a binomial articulation raised to some power is another factor of the binomial development.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





