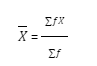The arithmetic mean, often known as the mean or arithmetic average, is a mathematical concept. When you add up all of the numbers in a data collection, you divide the total number of items in the data set by the total number of numbers in the data set. When integers are uniformly distributed, the arithmetic mean (AM) is equal to the number that is in the middle. In addition, the AM is calculated using a variety of approaches that are dependent on the amount of data and the distribution of the data being considered.
Arithmetic mean
The arithmetic mean is the most often seen and widely used metric of central tendency. In statistical terms, it is defined as the sum of all observed values divided by the number of observed values. It is commonly symbolized by the letter X. As a rule of thumb, if there are N observations, denoted by the X1 , X2 , X3, …, XN , then the Arithmetic Mean is given by
X = [X1 + X2+, X3+ …,+ XN ] / N
Right hand side can be written as
Here, i is an index which takes successive values 1, 2, 3…N.
The Calculation of the Arithmetic Mean
Generally speaking, there are two broad areas in which to study the calculation of arithmetic mean:
1. For ungrouped data, the arithmetic mean is used.
2. Arithmetic Mean for a Set of Observations
A Series of ungrouped data is represented by the arithmetic mean.
Method Using Direct Instructions
By using the direct technique, the arithmetic mean is defined as the sum of all observations in a series divided by the total number of observations.
Assumed Mean Method
In case the number of observations of the provided data is large then it is really difficult to find the arithmetic mean by doing the sum of observations i.e. using the direct method. In such a case, we have another method known as the assumed mean method. To reduce time when calculating the mean from a large number of observations and large numerical values, you can use the assumed mean method. On the basis of logic/experience, you consider a certain figure in the data to be the arithmetic mean. Then, for each observation, you can compute deviations from the stated assumed mean. Then, you can divide the sum of these variances by the number of observations in the data. The true arithmetic mean is calculated by adding the assumed mean and the ratio of the sum of deviations to the total number of observations.
For Grouped data Discrete Series
Direct Method
In the case of discrete series, the frequency shown against each observation is multiplied by its value. The resulting numbers are added together and divided by the total number of frequencies. Symbolically,
Where, Σ fX = sum of the product of variables and frequencies. Σ f = sum of frequencies.
Assumed Mean Method
As with individual series, the calculations can be simplified by modifying the previously described assumed mean technique.
Because the frequency (f) of each item is specified here, we can calculate fd by multiplying each deviation (d) by the frequency.
Then we get Σ fd. The next step is to get the total of all frequencies i.e. Σ f. Then find out Σ fd/Σ f. Finally, the arithmetic mean is calculated by X = A+ ∑fd/∑f using the assumed mean method.
Step deviation method
The variances are split by the common factor ‘c’ in this case, which simplifies the calculation. Here, we make an estimate d’ = d/c =X-AC in order to make numerical figures smaller for easy calculation. After that, obtain fd’ and ∑fd’. X = A + ∑fd’ / ∑f x c
The formula for calculating the arithmetic mean using the step deviation approach is as follows:
Continuous series
Class intervals are specified here. Calculating the arithmetic mean in the case of a continuous series is identical to that of a discrete series. The only distinction is that the midpoints of various class intervals are calculated. As previously stated, class intervals might be either exclusive or inclusive, or of uneven size. For instance, consider the intervals 0–10, 10–20, and so forth. For instance, consider the inclusive class intervals 0–9, 10–19, and so forth.
Uneven class intervals include, but are not limited to, 0–20, 20–50, and so on. In each of these instances, the arithmetic mean is calculated similarly.
Two intriguing features of A.M. are as follows:
the total of items’ departures from the arithmetic mean is always equal to zero.
extreme values have an effect on the arithmetic mean. Any large value, on either end, has the ability to move it up or down.
Conclusion
The central tendency statistic summarises the data into a single value that may be used to represent the whole set of data. Arithmetic mean is defined as the sum of all observed values divided by the total number of observed values. The sum of all items’ departures from the arithmetic mean is always zero. At times, it is necessary to assign weights to various elements based on their relative value. The arithmetic mean is the most often seen and widely used metric of central tendency. In statistical terms, it is defined as the sum of all observed values divided by the number of observed values. The AM is calculated using a variety of approaches that are dependent on the amount of data and the distribution of the data being considered. 2. Arithmetic Mean for a Set of Observations
Discrete Series, the frequency shown against each observation is multiplied by its value. The true arithmetic mean is calculated by adding the assumed mean and the ratio of the sum of deviations to the total number of observations. Calculating the arithmetic mean in the case of a continuous series is identical to that of a discrete series for Grouped data.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out