The name “parallelogram” comes from the Greek word “parallelogrammon,” which means “bounded by parallel lines. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with parallel lines on all sides as a result. It’s a shape with parallel and equal sides on both sides. Parallelograms are divided into three types: square, rectangle, and rhombus, each with its own set of characteristics.
The total number of unit squares that can fit into a parallelogram is measured in square units, and the area of a parallelogram is the total number of unit squares that can fit into it. like cm2, m2, in2, etc. In two-dimensional space, it is the region enclosed or encompassed by a parallelogram. A parallelogram is a four-sided, two-dimensional figure with the following properties:
Two equal and opposing sides,
Two intersecting but non-equal diagonals,
Two equal and opposite angles
Parallelogram Types
Based on its many features, a parallelogram can be categorized into several types. It is mostly divided into three categories:
Rectangle – All of the angles of a parallelogram are right angles, and the diagonals are equal.
Square – A parallelogram has all of its sides equal and all of its angles are 90 °.
Rhombus – All sides of a parallelogram are equal.
Parallelogram properties
There are six key properties of parallelograms listed below:
Opposite sides are congruent (AB = DC).
Oppositional angles are congruent (D = B).
The angles that follow each other are supplementary (A + D = 180°).
If one angle is correct, all angles are correct.
The diagonals of a parallelogram cut each other in half.
A parallelogram is divided into two congruent halves by each diagonal.
How to find the area of a parallelogram step by step
A parallelogram’s area is calculated by multiplying its base by its altitude. A parallelogram’s base and altitude are perpendicular to one another, as seen in the diagram below. As a result, the formula for calculating the area of a parallelogram is as follows:
To calculate the area, multiply the base of the parallelogram by the height.
The length of the long, flat side, or base, should be measured or recorded.
Draw a straight line from the base to the side that is parallel to it.
For height, measure the distance between your base and the top of the parallelogram.
To calculate the area, multiply the base by the height.
For the proper answer, always add “units squared” at the conclusion of your issue.
Area of parallelogram diagonal formula
Diagonal: A diagonal is a non-edged line segment that links two corners of a polygon. As a result, we can connect any two vertices that are not connected by an edge to form a diagonal.
The length of a parallelogram’s diagonals is calculated using the diagonals of a parallelogram formula.
Using the lengths of the sides and any of the known angles, this formula can be used to find the diagonal lengths.
The length of the diagonals of any parallelogram abcd can be calculated using the following formula:
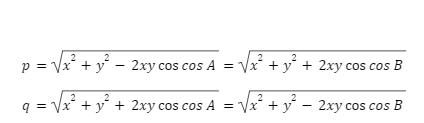
Where,
The lengths of the diagonals are denoted by p and q, respectively.
The parallelogram’s sides are x and y .
Another method for determining the lengths of the parallelogram’s diagonals and sides is to use a different formula.
Where, The diagonals’ lengths are p and q, respectively.
The parallelogram’s sides are x and y.
Example
How do you find the diagonal of a parallelogram with sides of 2 cm and 6 cm and a 450 angle?
Solution: Given the parameters a=2cm, b=6cm, and A=450,
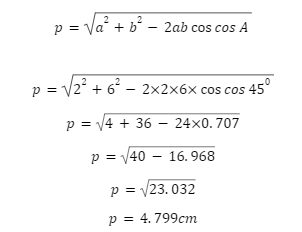
Conclusion
The opposite sides of a parallelogram are of equal length, and the opposite angles are of equal measure. The area of a rectangle and the area of a parallelogram are the same since the rectangle and the parallelogram share the same properties. Parallelograms have four straight sides to a parallelogram. Each of the two opposing pairs of sides is the same length and parallel. The parallelogram’s important characteristics have been widely used in industry to properly transfer linear force from one location to another.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



