Analytical study of the differential equation was initially proposed independently by Issac Newton and Leibniz in the late 17th century. These scholars made use of the concept of infinitesimal differences or distances in the Cartesian coordinate system, and the study was later generalised to the study of calculus. More developments in the study of calculus led to the study of differential equations.
Using differential equations, one can find the points of minima and maxima, which are in a system, whether the equation is increasing or decreasing, concave up or concave down. The study can be further generalised to be applicable to a number of practical problems. This includes calculating the flow of electricity, studying the motion of a to-and-fro object like a pendulum, studying thermodynamic systems, etc.
Rate of Change
When we calculate the derivative of y with respect to x, the practical implication of the term means the rate of change of the variable x with respect to independent variable x(dydx). Therefore, the rate of change of any variable can be calculated with respect to a given independent variable using derivatives.
Put more briefly, the rate of change is used to describe an instantaneous change (dy) in a variable y when there is a change dx in the independent variable y.
Question 1: Application of Differential Equations
Let us consider a cube whose volume is increasing at a rate of 9 cm per second. Calculate the rate of change of the increase in the surface of the cube when the length of the side of the cube is 10 cm.
Solution
Let us consider the length of the side of the cube to be x, S be the given surface area, and V be the given volume of the cube.
Therefore, the volume of the cube is expressed as V=x3, and the surface area is represented as S=6x2.
Here, x is a variable that is changing with respect to time.
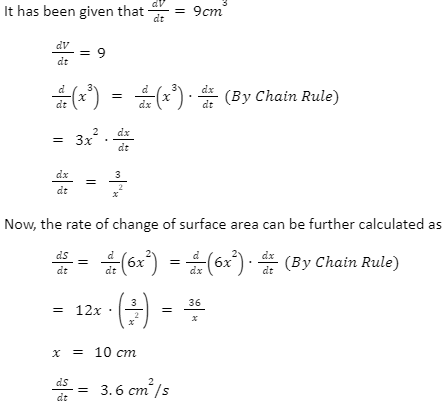
Maxima or Minima
The study of the differential equations can also be used to evaluate whether the function is increasing or decreasing. The derivative of dydx is positive if y increases as x increases and is negative if y decreases as x increases.
Question 2: Application of Differential Equations
Consider a rectangular body whose width is increasing at a rate of 2 cm per minute and the length is decreasing at a rate of 3 cm per minute.
Find the rate of changes of:
- The perimeter
- Area of the rectangle when the length is 10 cm and width is 6 cm.
Solution:
It has been given that the length x is decreasing and the width y is increasing with respect to the time variable.
Therefore, we get:

Modeling of Mathematical Systems
The system of the differential equations can also be used to model various systems subjected to numerous conditions and approximations. In this study, simulations are generally made with respect to certain parameters and initial conditions. The study is widely used by various scientists and engineers to model systems like:
- Population growth
- Logistic growth
- Predator-Prey equilibrium systems
- Star formation models
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






