Vector notation is a popular notation in mathematics and physics for representing vectors, which might be Euclidean vectors or, more broadly, members of a vector space.
The standard typographic approach for showing the vector is lower case, upright boldface font, as in v. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) suggests using a bold italic serif, such as v, or a non-bold italic serif with a right arrow emphasis. Vectors are frequently represented in advanced mathematics as a basic italic font, just like any other variable.
Unit Vector Notation:
The sign “^”, which is often known as a cap or hat, is used to denote a vector. It is provided by a^ = a/|a|, where |a| stands for the vector a’s norm or magnitude.
Three-dimensional unit vector:
The unit vectors of i, j, and k are commonly the x-, y-, and z-axes respectively. A linear combination of these unit vectors can be used to express any given vector in three-dimensional space. The cross-product of two supplied unit vectors, on the other hand, produces a third vector that is perpendicular (orthogonal) to both of them.
Normal Vector Unit:
A ‘normal vector’ is perpendicular to the surface at a specific point vector. A surface containing the vector is also referred to as “normal.” The unit normal vector, sometimes known as the “unit normal,” is the unit vector obtained after normalizing the normal vector. A non-zero normal vector is divided by its vector norm for this.
Set notation in order
An ordered collection of components surrounded in parentheses or angle brackets can be used to specify a rectangular vector in Rn.
V = (v1, v2 , v3 , v4 ,…, vn-1 , vn)
V= < v1, v2 , v3 , v4 ,…, vn-1 , vn >
V = [ v1, v2 , v3 , v4 ,…, vn-1 , vn]
Polar vectors:
A two-dimensional vector is made up of the two polar coordinates of a point in a plane. A polar vector has two components: a magnitude (or length) and a direction (or angle). The magnitude, which is usually written as r, is the distance between the origin and the point is represented. The angle (the Greek letter theta) is the angle formed by a fixed direction, generally the positive x-axis, and the direction from the origin to the point. It is normally measured counterclockwise.
Direct notation
Simplified autonomous equations that describe r and explicitly can also be used to specify polar vectors. This is cumbersome, but it avoids the misunderstanding that might emerge when using ordered pair or matrix notation with two-dimensional rectangular vectors.
Cylindrical Vector:
A cylindrical vector is a three-dimensional expansion of the idea of polar vectors. In the cylindrical coordinate system, it resembles an arrow. A cylindrical vector is defined by its xy-plane distance, angle, and distance from the xy-plane. The first distance is the magnitude of the vector’s projection onto the xy-plane, which is commonly written as r or ρ (the Greek letter rho). The angle is calculated asθ or φ(the Greek letter phi) the offset from the line collinear with the x-axis in the positive direction, and is commonly lowered to lie within the range 0 which is less than equal to the angle theta less than twice of pi. The second distance, commonly denoted by h or z, is the distance between the xy-plane and the vector’s terminus.
Notations for ordered sets and matrices
The second distance component is concatenated as a third component to construct ordered triplets (again, a subset of ordered set notation) and matrices, much as it is for polar vectors. The angle symbol can be used to prefix the angle; the distance-angle-distance combination differentiates cylindrical vectors from spherical vectors in identical notation.
Direct notation
A cylindrical vector can alternatively be defined directly using simplified autonomous equations that determine r (or ρ), θ (or φ), and h (or z). When naming variables, consistency should be used; for example, should not be confused with and so on.
Conclusion:
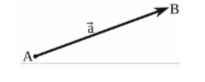
The quantity with both magnitude and direction are known as vectors. A vector is represented as a line with an arrow pointing in the direction of the vector, and the length of the vector denotes its magnitude. Vectors are therefore represented by arrows and have both beginning and terminal locations.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out