The verb “to touch” is referred to as “tangent.” The same concept is expressed using the Latin word “tangere.” In general, we can say that a tangent is the line that intersects the circle exactly at one point on its circumference but does not enter the circle anywhere inside of it. Tangents can branch off of a circle in multiple places. They are oriented such that they are perpendicular to the radius. In this article, let us delve deeper into the meaning of tangents as well as the theorems associated with them.
Tangent Meaning
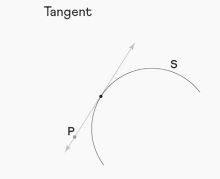
In the field of geometry, a tangent is a line that is drawn from an external point and passes through a point that is located on a curve. When you ride a bicycle, every point on the circumference of the wheel makes a tangent with the road. This is one example of a tangent that can be seen in real life. First, let’s take a look at a concrete illustration of the tangent concept. The following diagram illustrates a point P that is located outside of the arc S. P has been used as a point of departure in drawing a tangent to S. This is an illustration showing how a tangent might be represented.
A line is said to be tangent to a curve or curved surface in geometry if it touches that curve or surface at exactly one point. This definition comes from the field of geometry.
Tangent of a Circle
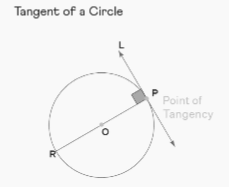
One way to define a tangent of a circle is as a straight line that touches or intersects the circle at exactly one point. Tangents are also known as chords. A line that touches the circumference of a circle but does not penetrate its interior is called a tangent. The diagram that follows demonstrates a circle with a point denoted by P. It has been determined that the tangent L goes through point P. An illustration of a tangent to a circle is shown here.
Point of Tangency
The only point at which a straight line touches or enters a circle is known as the point of tangency, and it is defined as the point where the two lines intersect. In the illustration that was just presented, the point P denotes the tangency point.
Tangent Properties
The tangent possesses two important properties, which are as follows:
- A curve is only touched by a tangent at one point along its length
- A line that touches the circumference of a circle but does not penetrate its interior is called a tangent
- At the point of tangency, where a right angle is formed with the circle’s radius, the tangent makes contact with the radius
A tangent to the circle has mathematical theorems associated with it, and these theorems are used when doing major calculations in geometry. In addition to the properties that have been listed above, these theorems can be found here.
The Formula for the Tangent of a Circle
Let’s move on to the next topic and study the equation of the tangent. A tangent is a line, and in order to write an equation for a line, we need two things: the slope of the line, which is denoted by “m,” and a point on the line. The equation for the tangent to a circle in general is as follows:
1) The equation y = mx ± a √[1+ m²] is the line equation that gives the tangent to the circle equation x² + y²= a² for a line that has the equation y = mx + c.
2) The equation x²+ y² = a² is a circle, and the tangent to that equation at the point (a1, b1) is xa1 +yb1 = a².
Therefore, the equation of the tangent can be written as follows: xa1+yb1 = a², where (a1, b1) are the coordinates used to calculate the tangent.
Conclusion
In the field of geometry, a tangent is a line that is drawn from an external point and passes through a point that is located on a curve. When you ride a bicycle, every point on the circumference of the wheel makes a tangent with the road.A line is said to be tangent to a curve or curved surface in geometry if it touches that curve or surface at exactly one point. This definition comes from the field of geometry.The only point at which a straight line touches or enters a circle is known as the point of tangency, and it is defined as the point where the two lines intersect.A curve is only touched by a tangent at one point along its length.A line that touches the circumference of a circle but does not penetrate its interior is called a tangent.At the point of tangency, where a right angle is formed with the circle’s radius, the tangent makes contact with the radius.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out