Vectors are two-dimensional geometrical entities with magnitude and direction. A vector’s magnitude is determined by its length, which is expressed by a line with an arrow pointing in the direction of the vector. As a result, vectors are represented by arrows, and they have initial and terminal points. Over the course of 200 years, the concept of vectors evolved. Vectors are used to represent physical quantities like displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Furthermore, with the advent of the field of electromagnetic induction in the late nineteenth century, the use of vectors began.
Vectors Meaning
A vector is derived from the Latin word vector, which means “carrier.” Vectors transport a point A to a point B. The magnitude of the vector is the length of the line connecting two points A and B, and the direction of the displacement from point A to point B is the direction of the vector AB. Vectors can also be referred to as Euclidean vectors or Spatial vectors.
Vectors can be subjected to a variety of operations, including addition, subtraction, and multiplication. In this section, we will look in depth at vector operations.
Vector Representation
Vectors are typically represented by a bold lowercase letter, such as , or by an arrow over the letter, such as a. Vectors can also be identified by their initial and terminal points, which are indicated by an arrow above them.
For example: vector AB denoted as AB a vector’s standard form of representation is A=a i+bj+ck a,b,c are real numbers, and i,j,k are the unit vectors along the x, y, and z axis, respectively.
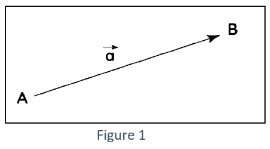
The initial point of a vector is also known as the tail, while the terminal point is known as the head. Vectors describe how an object moves from one location to another. Vectors can be represented by ordered pairs in the cartesian coordinate system. An ‘n’ tuple can also be used to represent vectors in ‘n’ dimensions. Vectors can also be identified by a tuple of components that represent the scalar coefficients for a set of basis vectors. The basis vectors are denoted as follows: e1 = (1,0,0), e2 = (0,1,0), and e3 = (0,1,0).
Types of Vectors
The following are some vector types:
Zero Vectors
Vectors with zero magnitude are referred to as zero vectors and are denoted by the symbol 0= (0,0,0). The zero vector has no magnitudes and no directions. It is also known as vector additive identity.
Unit Vectors
Unit vectors, denoted by a, are vectors with magnitude equal to one. Vector multiplicative identity is another name for it. A unit vector’s magnitude is one. It is commonly used to indicate the direction of a vector.
Position Vectors
Position vectors are used in three-dimensional space to determine the position and direction of movement of vectors. The magnitude and direction of position vectors can be changed in relation to other bodies. It is also known as the location vector.
Equal Vectors
If the corresponding components of two or more vectors are equal, they are said to be equal. Equal vectors are those with the same magnitude and direction. They can have different starting and ending points, but their magnitude and direction must be the same.
Negative Vector
The inverse of two vectors is when their magnitudes are the same but their directions are opposite. If vectors A and B have the same magnitude but opposite directions, vector A is said to be the inverse of vector B, and vice versa.
Parallel Vectors
Parallel vectors are two or more vectors that have the same direction but not necessarily the same magnitude. The angles of direction of parallel vectors differ by zero degrees. Antiparallel vectors are those whose angles of direction differ by 180 degrees; that is, antiparallel vectors have opposite directions.
Orthogonal Vectors
If the angle between two or more vectors in space is 90 degrees, they are said to be orthogonal.
Co-initial Vectors
Vectors with the same initial point are referred to as co-initial vectors.
Examples of Vector
Velocity, momentum, force, electromagnetic fields, and weight are examples of vectors found in nature.A scalar quantity or phenomenon is one with only magnitude and no direction.
Conclusion
We conclude in this article that, a vector is a two-dimensional object with a magnitude and a direction. A vector can be visualized geometrically as a directed line segment with an arrow indicating the direction and a length equal to the magnitude of the vector. The vector’s orientation is from tail to head. Vectors are used in a variety of real-world situations, including those involving force or velocity.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






