The difference between any two consecutive terms in an arithmetic progression or arithmetic sequence is always the same. The common difference, denoted by d, is the difference between the consecutive terms. An arithmetic progression is a set of numbers in which each term is derived from the one before it by adding or subtracting a fixed number called the common difference “d” from the previous term.
The sequence 9, 6, 3, 0,-3… For example, is an arithmetic progression with -3 as the common difference. The Arithmetic Progression (AP) -3, 0, 3, 6, 9 is an AP with 3 as the common difference.
Sequence
A list of numbers in a specific order is known as a sequence or progression. It’s a series of numbers that follow a specific pattern, and the elements of a sequence are referred to as terms. There are many different types of universally accepted sequences, but the one we’ll look at right now is the arithmetic progression.
Arithmetic Progression
An arithmetic progression, also known as an arithmetic sequence, is a set of numbers in which the difference between successive terms remains constant.
General Form of AP
An Arithmetic Progression can take the following forms: a, a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d, and so on.
Tn = a + (n – 1) d is the nth term of an AP series, where Tn is the nth term and an is the first term. Tn – Tn-1 = d = common difference
Sum of n terms in Arithmetic Progression
The formula below can be used to calculate the sum of the first n terms in arithmetic progressions.
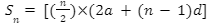
The sum is Sn, the number of terms in AP is n, the first term is a, and the common difference is d.
When we know the first and last terms of AP, a and l. The result is the sum of n terms.
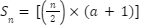
Formula derivation
Assume that ‘t’ is the nth term in the series and that Sn is the sum of the first n terms in the following arithmetic progression: a, (a + d), (a + 2d),…, a + (n – 1)× d.
Sn= a1 + a2 + a3 + ….an-1 + an
We get by substituting the terms in the formula above.
Sn= a + a + d+ a + 2d+…. + (t – 2d) + (t – d) + t …….(1)
After reversing the order of the equation (1),
Sn =t + t – d+ t – 2d+ …….. + a + 2d+ a + d……(2)
When equations (1) and (2) are combined, we get
2Sn = (a + t) + (a + t) + (a + t) + …….. + (a + t) + (a + t) + (a + t)
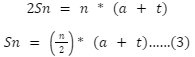
If we replace the last term ‘t’ in equation (3) with the nth term, we get:
nth Term = a + (n – 1) * d
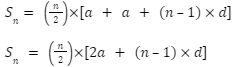
If l is the last term of a finite Arithmetic Progression say with n terms, and an is the first term, then S=2n(a+l) is the sum of all terms of the A.P.
List of Formulas for Arithmetic Progression
The following arithmetic progression formulas are listed in the table below:

Conclusion
In this article we conclude that an arithmetic progression is a sequence of numbers in which the difference between two consecutive terms is always the same. In our daily lives, we can see many examples of arithmetic progression. By analyzing a specific pattern, such as AP used in straight line depreciation, arithmetic progression can be applied in real life.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






