When a plane slices the cone at an angle with the bottom, the ellipse is one of the conic sections that results. A circle is formed when the cone is intersected by a plane parallel to the bottom.
The set of all points where the sum of the distances between two fixed points is constant is called an ellipse. To put it another way, there are two fixed points known as foci. We can construct an ellipse by tracing out all places where the distance between the primary focus and a point, as well as the distance between the secondary focus and the same point, remains constant.
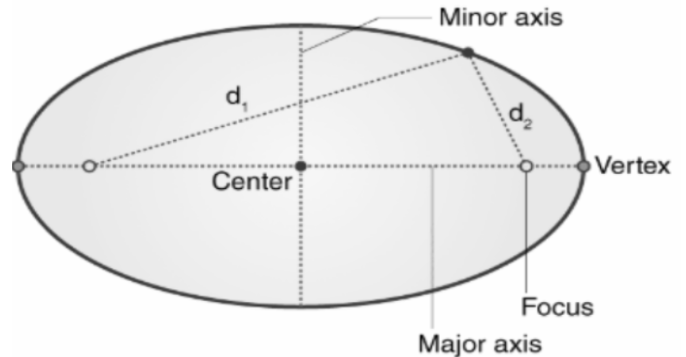
Properties of Ellipse
Ellipse contains two focal points, called foci, and the directrix is a set distance parallel to the latus rectum and perpendicular to the major axis
The eccentricity of an ellipse ranges from 0 to 1
The total sum of any distance between an ellipse’s locus and its two focal points is constant
Ellipse has one major and minor axis, as well as a center
Major and Minor Axes (Principal Axes)
The major axis is the ellipse’s longest diameter (typically represented as ‘a’), which runs through the centre from one end to the other at the ellipse’s broadest point. The minor axis (denoted by ‘b’) is the ellipse’s shortest diameter, passing through the centre at its narrowest point. Half of the major axis is the semi-major axis, and half of the minor axis is the semi-minor axis.
Linear Eccentricity
It is the distance between the ellipse’s centre and any focus. The linear eccentricity formula is
c = √a2-b2
Eccentricity
The ellipse’s eccentricity can be computed using the formula:
e = c / a = √(1 – (b2 / a2))
Semi Latus Rectum
The latus rectum is the length of a chord passing through one focus perpendicular to the major axis. The semi-latus rectum makes up half of it. Semi Latus Rectum has the following formula:
l = b2 / a = a(1 – e2)
Ordinate and Double Ordinate
Allow P to be any point on the ellipse, and PN to be perpendicular to the major axis AA’, so that the PN created meets the ellipse at P’. The ordinate of P is thus PN, and the double ordinate of P is PNP’.
Equation for an Ellipse (Standard Form)
The ellipse equation is written in its conventional form as:
(x-h)2 / a2 + (y-k)2 / b2 = 1
where (h , k) is the ellipse’s centre and a and b are the semi-major and semi-minor axes’ lengths, respectively.
If the origin is used as the centre, the equation becomes:
x2 / a2 + y2 / b2 = 1
Auxiliary Circle
If b equals a in the usual form of the elliptical equation with its centre at origin, the equation becomes:
x2 + y2 = a2
The circle described on the major axis of an ellipse as diameter is known as the auxiliary circle of the ellipse.
Director Circle
A director circle is the point of intersection of perpendicular tangents to an ellipse. If an ellipse’s equation is x2 / a2 + y2 / b2 = 1, then the director circle’s equation is:
x2 + y2 = a2 + b2
Area of an Ellipse
The area of an ellipse is denoted by Aellipse which is calculated by using the formula:
Aellipse= ℼab
Perimeter of Ellipse
The complete distance around an ellipse’s outside boundary is its perimeter. It’s simple to find the circumference of a circle since the distance from the centre to any point on the circle’s locus is the same. The radius is the measurement of this distance.
In the case of an ellipse, however, we have two axes, major and minor, that intersect in the centre. As a result, we utilise an approximation formula to calculate the perimeter of an ellipse:
Pellipse = 2ℼ √((a2 + b2) / 2)
where a and b are the lengths of the semi major axis and semi minor axis respectively.
Applications of Ellipse
They have several uses in engineering, physics, and other fields. For instance, all planets revolve in elliptical orbits. Furthermore, astronomy makes extensive use of this form, as many stars and planets are ellipsoids.
Conclusion
A ‘conic’ curve is formed by intersecting a right circular cone with a plane. In Euclidean geometry, it possesses unique features. The vertex of the cone separates the conic section into two nappes, the upper nappe and the lower nappe. A conic section is a locus of a point P travelling in the plane of a fixed point F known as focus and a fixed line d known as directrix (with the focus not on d) in such a way that the ratio of point P’s distance from focus F to its distance from d is a constant e known as eccentricity.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






