It is possible to take an accurate measure of the shapes or graphs that are finite or are of a definite shape. But what if the graph or shape of an object is not made up of straight lines? It is in that case that the integrals are needed. It is integrals that give an accurate measure of the area over or under a curve, or the line that makes up that curve. Integrals take into measure even the smallest value possible to attain and give out a value that is closest to the accurate value.
Definite Integral
A definite integral is an integral that gives a fixed value for a curve within the two given limits. And the value that we get out of this integral consists of every infinitesimal number or quantity that lies in between the two given limits.
The definite integral for a function f(x) is represented as follows:
∫baf(x)dx
where ‘b’ stands for the lower limit for the function f(x),
‘a’ is the upper limit for the function,
‘f(x)’ is the function of which integral is to be found,
‘dx’ is the reference of the function to the x-axis.
For the principle regarding this integral, the area under a curve is divided into infinitely many small rectangles, to get a precise outcome. The more the number of rectangles the area under the curve is divided into, the more accurate the outcome will be. This happens to be the basic theory that lies behind the application of definite integrals.
Hence, it can be stated that a definite integral is a nearly precise entity.
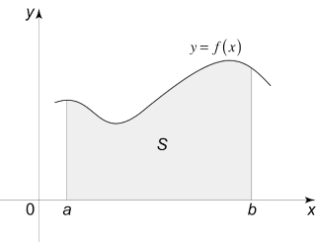
In the above-drawn function;
y = f(x)
It is not possible to calculate the area under the curve using general area methods. Hence, in such cases, definite integrals are needed.
Definite Integral Calculator
There are mainly two methods that are used to solve definite integrals. Those two methods happen to be as follows:
- Definite integral as a limit of the sum
- Finding definite integral using the fundamental theorem of calculus
Definite integral as a limit of the sum
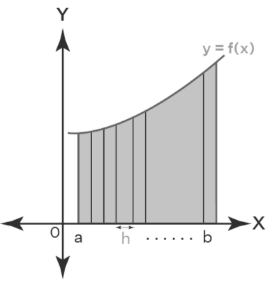
Let the function f(x) be divided into infinitely many small intervals. To find the definite integral of the function f(x) over limits a to b, all these intervals need to be taken into account.
Taking the number of intervals between ‘a’ and ‘b’ to be ‘n’, and the width of each interval to be ‘h’.
In this case,
h→0
n→∞
The distance of each interval from the y-axis can be expressed in the terms of the following A.P:
x0 = a, x1 = a+h, x2 = a+2h,… xr = a+rh, xn = a+nh = b
Here, ‘n’ can be given as:
n = (b – a)/h
Therefore, the sum is to be taken of every interval that comes under the curve, to find out the definite integral for a function. And that definite integral is given as follows:
∫abf(x)dx = limn→∞∑r=1nhf(a+rh)
where ‘h’ = (b-a)/n
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
In this method of solving the definite integral for a function, the values of the upper limit and lower limit for the integral are to be substituted in the antiderivative of the function f(x), also known as infinite integral, and then, subtracted in the respective order.
∫abf(x)dx = F(b) – F(a)
where f(x) = F'(x)
Definite Integral Properties
∫ab f(x) dx = – ∫ba f(x) dx
∫aa f(x) dx = 0
∫ac f(x) dx = ∫ab f(x) dx + ∫bc f(x) dx
∫ab f(x) dx = ∫ab f(a + b – x) dx
∫0a f(x) dx = f(a – x) dx
∫ab c f(x) dx = c∫ab f(x) dx
∫ab f(x) + g(x) dx = ∫ab f(x) dx + ∫ab g(x) dx
∫ab f(x) – g(x) dx = ∫ab f(x) dx – ∫ab g(x) dx
∫-aa f(x) dx = 0
If f(x) is an odd function.
f(-x) = -f(x)
∫-aa f(x) dx = 2∫0a f(x) dx
If f(x) is an even function.
f(-x) = f(x)
∫02a f(x) dx = 2 ∫0a f(x) dx
If f(2a – x) = f(x).
∫02a f(x) dx = 0
If f(2a – x) = – f(x)
Conclusion
The definite integral of a function gives us the accurate outcome for every value that might lie in between two limits to an infinitesimal decimal. Because of its high accuracy and precision, it is used to calculate areas, lengths and volumes of curves.
Using the fundamental theorem of calculus is the easiest and most effective way to calculate the definite integral of a function. It is easy to calculate and relies on simpler terms.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



