Introduction
The cartesian plane is a two-dimensional coordinate plane produced by the intersection of the x-axis and the y-axis in mathematics. At the origin, the x- and y-axes cross perpendicular to each other. In this post, we’ll look at what a cartesian plane is and how it’s made up of distinct elements. Rene Descartes, a French mathematician, is credited for formalizing its usage in mathematics.
Cartesian Plane
The cartesian plane is a two-dimensional coordinate plane made up of two perpendicular lines intersecting. The X-axis is the horizontal line, and the Y-axis is the vertical line. The horizontal distance from the origin is x, and the vertical distance is y, according to the coordinate point (x, y) on the Cartesian plane. The point is on the right of the origin if the sign of x is positive; otherwise, it is on the left. If the sign for y is positive, the point is y points above the origin; otherwise, it is y points below.
Axes
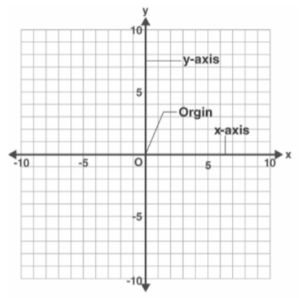
There are two axes in the cartesian plane. The horizontal axis is known as the x-axis, while the vertical axis is known as the y-axis.
Origin
The origin is the point where the x-axis and y-axis intersect in the cartesian plane. The origin is represented in the cartesian plane by an ordered pair or the cartesian coordinate (0, 0).
Cartesian Plane Quadrants
The X- and Y-axes divide the plane into four pieces, which are referred to as quadrants. In an anticlockwise manner, quadrants are labeled I, II, III, and IV. The plane’s axes are known as Cartesian axes, and the plane is termed the Cartesian plane.
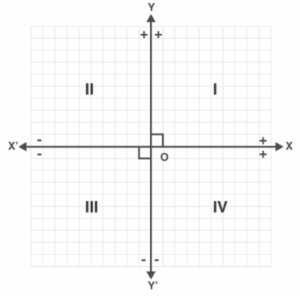
Here,
OX is the positive X axis; OX’ is the negative X axis. OY is the positive Y axis and OY’ is the negative Y Axis.
As a result, the quadrants are distinguished by the abscissa and ordinate signs:
- x > 0 and y > 0 or ( + , + ) quadrant
- x < 0 and y > 0 or ( – , + ) quadrant
- x < 0 and y < 0 or ( – , – ) quadrant
- x > 0 and y < 0 or ( + , – ) quadrant
The points on the axis can have any of the coordinates, such as (x, 0) or (y, 0). (0, y). The point is on the x-axis if the coordinate is of the form (x, 0), and the point is on the y-axis if the coordinate is of the form (0, y). The point is not in any of the quadrants in this situation.
Cartesian Coordinates
The cartesian coordinates are the ordered pair in the cartesian plane. The cartesian coordinates have the following format: (x, y). The abscissa and ordinate relate to the ordered pairings in the two-dimensional plane.
Abscissa
The abscissa is the first number in the ordered pair. In other words, the abscissa is the value of x in the ordered pair. It is the distance from the y-axis of any point on the plane.
Ordinate
The ordinate is the second number in the ordered pair. It uses the value of y as input. The ordinate is the distance from the x-axis of any point on the plane.
How to Plot Points in the Cartesian Plane?
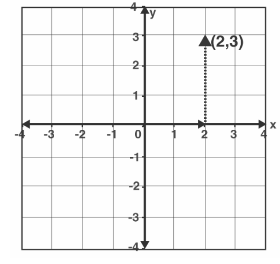
In the cartesian plane, plot point (2, 3)
First, from the supplied ordered pair, determine the abscissa (x-value) and ordinate (y-value). Abscissa = 2 and ordinate = 3 in this case.
Then, on the x-axis, plot the value of x (i.e. “2”). Because the value of x is positive, plot the number and move 2 units from the origin to the right.
Then, on the y axis, plot the value of y, which is “3.” Plot the number and move it 3 units higher on the y-axis from the origin, since it takes a positive value.
Finally, the point (2, 3) is found in the cartesian plane’s first quadrant.
Conclusion
A point’s coordinates, a pair of numbers enclosed in parenthesis, determine its location in the plane: (x,y). The first value, x, represents the point’s horizontal position, while the second, y, represents its vertical position. All positions are measured in relation to the origin, which is a “center” point whose coordinates are (0,0). The Cartesian plane extends in all directions indefinitely. Math textbooks commonly draw arrows at the ends of the axes to demonstrate this.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out