Before entering deep into the acylation mechanism concepts, we need to understand the meaning of the acylation mechanism and its importance. Acylation is also known as alkanoylation. It is a chemical reaction in which an acyl group will be added to a molecule or compound. The acyl group has a molecular formula of RCO, also called a functional group. An acylating agent is a compound that is contingent on the acyl group. When Acyl halides are treated with some metal catalysts, it acts as an acylating agent in the acylation mechanism. Acylation reaction is considered one of the major reactions in organic chemistry.
What is Acylation?
Think of an alkyl group that attaches to the CO in the acyl’s structure. The CO group represents carbonyl. A double bond joins the carbon and oxygen atoms in a carbonyl group.
We need an acylating agent and a catalyst to carry forward the reaction. The acyl group is considered an acylating agent in this scenario. This can be involved as a compound of the acyl group.
The catalyst, which has to be added, is a chemical that helps speed up the rate of the reaction. The catalyst will be there before and after the completion of the reaction.
Acylation Mechanism
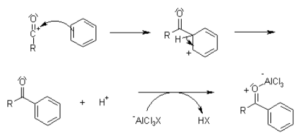
The acylation mechanism is the reaction that purely depends on the electrophilic aromatic substitution. As discussed earlier, acylation is the technique used to add an acyl group to a particular compound or molecule. This reaction consists of a nucleophile at the electrophilic carbonyl group of a carboxylic acid derivative.
Even though we have many acylating reagents, the most common reagents we use are halides and anhydrides. Alcohol ROH and phenols ArOH acts as the nucleophile in the acylation reaction. These nucleophiles increase ammonia or amines. In some cases, acyl halides will be used as acylating agents because it forms strong electrophiles if we add them with metal catalysts.
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
We can look into Friedel crafts acylation to understand acylation as an example. The acylating agent will be CH3COCl – acetyl chloride. And the compound it uses for the reaction is AlCl3 – Aluminium chloride. An acyl group, ethanol, or acetyl group will be added to make benzene.
The transformation of the aromatic ring happens in the Friedel crafts acylation reaction. It will be transformed into ketone. The acyl group will be attached to the carbon-oxygen double bond. And it also acts as an alkyl group.
An alkyl group is represented by “R”. The acyl group formula is RCO. The main process of acylation is substituting the acyl group in the reaction. For the most part, the ethanol group CH3CO is employed in the process.
Acylating amines commonly use carboxylic acids such as acyl halides and anhydrides as acylating agents to form amides. Acylate alcohols also form esters. As they are nucleophiles, this mechanism is called a substitution reaction of nucleophilic acyl. Acylation reactions widely use the most common succinic acid. Acylation occurs once the single compound is formed using the succinic’s salts.
To understand the Acylation mechanism‘s meaning and importance, we need to discuss the formula and reaction of the compounds involved. It is easy to understand the reactions and the combination of chemicals. The acylation process will prevent rearrangement reactions involved in the process of alkylation. The acylation reaction is involved in it to attain this reaction. Clemmensen reduction removes the carbonyl group using the same process.
To understand the concept in detail, let us see some simple examples.
Acetic acid, or the equivalent of acidic acid like vinegar, which has only 5 percent of acetic acid, is available in water in the form of chloride. This has a chemical structure CH3COCl and which is also called acetyl chloride.
Acylating benzene joins the process of catalyst aluminium chloride and gives the below reaction.
C6H6 + CH3COCl + catalyst → C6H5-CO-CH3 + HCl
As a catalyst, benzene is treated with ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl, and aluminium chloride. Phenylethanone, a ketone, is produced. Ketones are considered one of the essential compounds for the process of additional synthesis; especially, it offers many reaction paths for it.
Ultimately, acylation is considered an essential reaction for primary and secondary amines. In the above scenario, a hydrogen atom is reinstated by an acyl group. Reagents used in the scenario are anhydrides, acid chlorides, or even esters. The products captured amides of correlative acids.
Friedel crafts acylation has some limitations. Carbocation rearrangement can be made only with a few alkylbenzenes. Since nitrobenzene is a strong deactivating chemical, it fails to combine with such compounds.
Conclusion
Acylation reaction is mainly used to process biological applications. This applies to the chemical application also. Acylation reaction is used in various mechanisms involving tedious cellular processes and regulation. The applications of acylation reactions are many. It is widely used in pharmaceutical products. In some industries, acylation reactions also use chemicals to make plastic products. We shall conclude by answering a few acylation mechanism questions.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





