A nucleophile is a reactant in the equation that provides its electrons to the co-reactant to form new bonds in the chemical equation. It is primarily necessary to know what a Lewis base is to understand the concept of nucleophiles.
A Lewis base is any species with a filled orbital around the nucleus. It also includes a pair of electrons that it will tend to donate to a species seeking electrons to form new bonds, and this species is called Lewis acids.
Hence, when we state that a nucleophile is a Lewis base. It means that a nucleophile tends to donate electrons to any species that seek them, like electrophiles, to form new bonds.
The term ‘nucleophile’ literally means that it is nucleus loving. Nucleophiles have a negative charge since the nucleus has an overall positive charge, and opposites charges attract.
Difference between an Electrophile and a Nucleophile
Electrophile | Nucleophile |
They are species that seek to accept electron pairs. | They are species that seek to donate electron pairs. |
Electrophiles are electron loving. | Nucleophiles are nucleus loving. |
All electrophiles are Lewis acids. | All nucleophiles are Lewis bases. |
They include positive charged and neutral charged species. | They include negative charged and neutral charged species. |
They may appear in the form of electron-deficient atoms, molecules, or ions. | They may appear in the form of electron-rich atoms, molecules, or ions. |
It tends to undergo electrophilic addition and electrophilic substitution reaction. | It tends to undergo nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic substitution reaction. |
Importance of Nucleophiles
A nucleophile is as important as an electrophile. Both attract each other leading to the formation of new molecules and compounds. A nucleophile always goes hand in hand with an electrophile, as every electron donor needs an electron acceptor to form bonds.
Nucleophiles, typically for all intents and functions, are going to be both some negatively charged species or molecules with N, P, or S atoms.
Ways to Identify an Electrophile and a Nucleophile in a Chemical Reaction
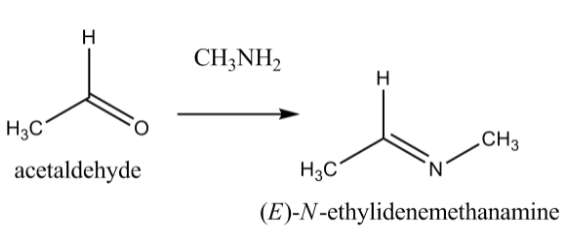
Let us understand how to identify an electrophile and a nucleophile in a chemical reaction from the example in the image. The image shows the reaction between acetaldehyde (an aldehyde) and methylamine (an amine).
Here, the nitrogen in the amine is the nucleophile as it donates electrons to the carbon in the aldehyde. Therefore, we can say that carbon is an electrophile because it accepts electrons. This reaction thus leads to the formation of a new bond.
Conclusion
Nucleophiles are an important part of any chemical equation. They provide a pair of electrons to the needing species, basically known as an electrophile. Consequently, there is the formation of new bonds, creating different molecules and compounds as products.
All nucleophiles are known to be Lewis bases, as they give up electron pairs to Lewis acids in a chemical reaction.
The most important nucleophile atoms are oxygen, nitrogen, and sulphur. The most critical nucleophilic functional groups that exist are water, alcohol, amines, thiols, phenols, and sometimes carboxylates.
We also understood how to identify the nucleophile in a reaction using an example.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





