Atomic orbitals are mathematical functions that describe the wave nature of electrons (or electron pairs) in an atom. They are also known as atomic orbitals.
In addition, they provide a method for calculating the probability of finding an electron in a specified region around the nucleus of an element’s nucleus.
Chemistry of Orbitals
It is possible to have four different kinds of orbitals, each with a different shape. These are denoted by the letters s,p,d, and f. The s and p orbitals are the only ones taken into consideration because they are the most common in organic and biological chemistry, respectively. It is spherical in shape with the nucleus at its centre, whereas a p-orbital is dumbbell-shaped, and four of the five d orbitals are cloverleaf in shape. d orbitals are shaped like an elongated dumbbell with a doughnut in the middle, and the fifth d orbital is no exception. The orbitals in an atom are organised into different layers or electron shells, which are referred to as electron shells.
Shape of s Orbital:

The boundary surface diagram for the s orbital has the shape of a sphere with the nucleus at its centre, which can be visualised as a circle in two dimensions when viewed from above.
In this way, we can say that s-orbitals are spherically symmetric, with the probability of finding the electron at a given distance equal in all directions regardless of the direction of the electron’s motion.
It is also discovered that the size of the s orbital increases with the increase in the value of the principal quantum number (n), with 4s > 3s > 2s > 1s being the largest.
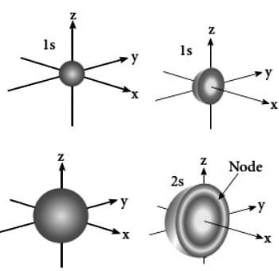
1s orbital:
The 1s orbital is the orbital that is closest to the nucleus in terms of distance. It has the least amount of energy compared to the other orbitals. It also has the distinction of being the smallest spherical shape. As a result, the radius of the s orbital is relatively small. In the s orbital, there can only be two electrons at a time. If there is only one electron in the s orbital, the electron configuration can be written as 1s1, which means there is only one electron in the s orbital. It can, however, be written as 1s2 if there are two electrons in the system. The two electrons in the s orbital then move in opposite directions as a result of the repulsion that occurs as a result of the same electrical charges carried by the two electrons in the s orbital. It is referred to as paramagnetic when there is an unpaired electron present. This is due to the fact that it can be attracted by a magnet. However, if the orbital is completely filled and there is a pair of electrons present, the electrons will not be attracted by a magnet; this is referred to as diamagnetic behaviour.
2s orbital:
The 2s orbital is larger than the 1s orbital. As a result, its radius is greater than that of the 1s orbital. It is the orbital that is closest to the nucleus after the 1s orbital. Its energy is higher than that of the 1s orbital, but it is lower than that of the other orbitals in an atom. The 2s orbital can also only be filled with one or two electrons. However, the 2s orbital is only filled with electrons after the 1s orbital has been completed. This is referred to as the Aufbau principle, and it indicates the order in which electrons fill sub-orbitals.
Conclusion:
It is possible for an atom to have many different numbers of orbitals, according to the quantum atomic theory. The sizes, shapes, and orientations of these orbitals can all be classified as well. With a smaller-sized orbital, there is a greater likelihood of attracting the attention of an electron close to the nucleus. When it comes to representing the coordinates of an electron, the orbital wave function, also known as,ϕ is used. The square of the orbital wave function,demonstrate the probability of finding an electron in the nucleus.
When drawing boundary surface diagrams, this wave function is also useful. The shape of orbitals can be better understood using boundary surface diagrams of the constant probability density for various orbitals.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





