Introduction
Boric Acid, which is also known as hydrogen borate, orthoboric acid and, boracic acid, is a weak acid. In fact, it is an acidic hydrate of boric oxide with mild, antifungal, antiseptic and antiviral properties. The precise mechanism of action of boric acid is unidentified; usually cytotoxic to all cells. It is generally used in the treatment of yeast infections and fever blisters (also known as cold sores). It is one of the utmost produced borates and is extensively used all around the world in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies, as a nutritious supplement, flame retardant (which help reduce fire damage on people), in the manufacturing of glass as well as fiberglass, and in the manufacture of timber preservatives to control pests.
Boric Acid As Boric Acid Powder
In our day-to-day life, we oftenly termed the boric acid as boric acid powder as it appears as a white powder. It is generally used as a pesticide i.e., for control of cockroaches. Actually it clings the cockroaches when they come in contact with this powder. This powder is also used as a fertiliser in crop fields, and also in detergents and hand soaps.
STRUCTURE OF BORIC ACID
The chemical structure of boric acid is generally known as H3BO3, sometimes which is also written as B(OH)3. From this formula we can easily see that, the compound contains one boron atom, three hydrogen and three oxygen atoms in which three -OH groups i.e., hydroxyl groups are attached to one boron atom. The structure of the compound is as depicted below:
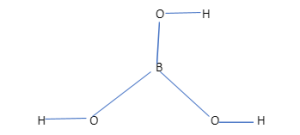
It has basically a two-dimensional structure, which lies on a plane. According to VSEPR theory, the molecular geometry of this compound is found to be trigonal planar.
Physical Properties
Some of the basic physical properties of Boric Acid are as follows:
- It has a molecular mass of 61.83 g/mol.
- It is a colourless and odourless substance.
- It is generally a white crystalline solid at room temperature i.e., at 250C.
- It is fairly soluble in water. The solubility of boric acid in water in room temperature is 57 grams per litre.
- It is also slightly soluble in acetone and sparingly soluble in pyridine.
- The boiling point of Boric Acid is 5000C (or 5730F).
- The melting point of this compound is 170.900C(or 339.620F).
- It has a density of 1.43 g/cm3.
Chemical Properties
- Heating:
- Heating boric acid at 1700C gives metaboric acid. The reaction is as: H3BO3 → HBO2 + H2O
- While it gives tetraboric acid on heating at 3000C. The reaction is as: 4HBO2 → H2B4O7 + H2O
- But at 3300C, it gives boron trioxide on heating. The reaction is as: H2B4O7 → 2B2O3 + H2O
- It easily got dissolved in sulphuric acid whose reaction is as follows: B(OH)3 + 6H2SO4 → B(HSO4)4- + 2HSO4- + 3H3O+
- It reacts with alcohols to give borate esters. The reaction is as given below: B(OH)3 + 3ROH → B(OR)3 + 3H2O
- It forms sodium metaborate and tetraborate when reacts with NaOH.
- It does not get completely ionised in water or any other solvents.
Preparation Of Boric Acid
Boric acid might be prepared by reacting borax (sodium tetraborate decahydrate) with a mineral acid, for example hydrochloric acid(HCl):
Na2B4O7·10H2O + 2HCl → 4 B(OH)3 + 2 NaCl + 5 H2O
It can also be formed as a by-product of hydrolysis of boron trihalides and diborane. The reaction is as:
B2H6 + 6H2O→ 2B(OH)3 + 6H2
BX3 + 3H2O → B(OH)3 + 3HX (X = Cl, Br, I)
Uses Of Boric Acid
Generally, now a days this compound is widely used in many industries and factories. Let us see about few of its uses:
- It is typically used in the manufacturing of glass and monofilament fibreglass.
- It is used in combination with denatured alcohol in jewellery industries.
- It is also used in electroplating.
- It is used in manufacturing flat LCD panel displays.
- Sometimes it is also used as a fire retarding agent, which helps in reduction of fire damage on people.
- It is also used by blacksmiths in welding flux.
- It is used as an antiseptic, insecticide as well as a neutron absorber.
- The mixture of boric acid along with vegetable oils or petroleum works as an excellent lubricant.
- It is also used in swimming pools as a primary buffer.
- This compound has also a great role in agriculture sector i.e., it is used to prevent boron deficiency and also used in preservation of grains such as rice and wheat etc.
- It is also used in many industries to counteract the harmful effects of hydrofluoric acid (HF).
- It is also used in treatment of ear infection in case of both humans and animals.
- This acid mixed with distilled water is also used as a would spray which helps in blood clotting.
These are few of the uses of boric acid, but apart of all these uses there are also many more industrial as well as household uses of boric acid.
Conclusion:
Boric acid and its sodium borate salts are insecticides found in nature and in a variety of industries. One of the most frequent products is borax. Boric acid and its sodium counterparts have various ways of combining boron with other elements. Their toxicity is mostly determined by the quantity of boron they contain.
Boric acid and its sodium counterparts are effective against a wide range of pests. Insects, spiders, mites, algae, moulds, fungi, and weeds are among them. Since 1948, products containing boric acid have been registered for use in the United States.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





